Index

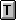
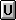
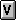
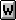
- $ in Indicator Area
- 5.3.3 Syntax
- %TMP%, using in place of a file name
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- .def files
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- 132-column mode:configuration variable
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- 132-column mode:using escape sequences to switch
- 6.2.2 Terminal Manager Restrictions
- 132-column mode:using the 132-MODE variable
- 132-MODE
- 132-column mode:via DISPLAY verb
- DISPLAY SCREEN SIZE
- 132-mode
- DISPLAY Statement
- 3-D, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- 3D-LINES
- 9.9.2 Drawing 3-D Lines
- 3D-LINES
- 6.8.8 Thread Interaction with Run Units
- 6.8.8 Thread Interaction with Run Units
- 7-BIT
- 7-BIT
- 80-column mode via DISPLAY verb
- DISPLAY SCREEN SIZE
A
- A_CGI environment variable
- 6.9.2 A_CGI Environment Variable
- A_CONFIG, and PC-based LANs
- A.3.2.3 Using A_CONFIG
- a_termcap
- A.2.2 Terminal Database
- 4.2.1 Step one-Terminal Identification
- A_TERMS.DAT
- A.2.2 Terminal Database
- Abbreviated Combined Condition
- Abbreviated Combined Condition
- abbreviated combined condition, language skeleton
- Abbreviated Combined Condition
- abbreviated combined relation conditions
- 6.3.8 Abbreviated Combined Relation Conditions
- abort, graceful
- 6.7 Exiting from ACUCOBOL-GT Programs
- ACCEPT
- ACCEPT
- 5.9.1 PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- ACCEPT ALLOWING MESSAGES
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- ACCEPT and DISPLAY, example using Screen Section
- 6.5.4 Comparison to Field-level
- ACCEPT BEFORE TIME
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- ACCEPT FROM ENVIRONMENT
- H.1 Introduction
- ACCEPT FROM STANDARD OBJECT, to get a font handle
- 4.6 Fonts
- ACCEPT FROM SYSTEM-INFO:Windows
- M.2.5 Differences between MS-DOS and Windows
- ACCEPT FROM SYSTEM-INFO:Windows NT
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- ACCEPT statement, different forms summarized
- ACCEPT Statement
- ACCEPT statement, embedded procedures
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- ACCEPT statement, syntax rules
- ACCEPT Statement
- ACCEPT, and color
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- ACCEPT, and menus
- 8.6 Menu Input
- ACCEPT, EXCEPTION clause
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- ACCEPT, screen options
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- ACCEPT: pre-defined exception values
- ACCEPT Statement
- ACCEPT:activating a control
- 3.5 Entering Data into a Control
- ACCEPT:ALLOWING MESSAGES
- 6.8.3 Thread Communication
- ACCEPT:effect on floating window
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- ACCEPT-CONTROL field
- 6.0 Events Reference
- ACCEPT statement, general format
- ACCEPT Statement
- ACCEPT-TIMEOUT
- ACCEPT-TIMEOUT
- ACCESS MODE
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- ACTION, GRID special property
- 5.15 Grid
- active and current windows
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- active window
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- ACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR
- ACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR
- Acu4GL
- 1.1 Product Overview
- ACUCOBOL
- ACUCOBOL
- ACUCOBOL-GT Development Suite, installing from CD-ROM
- A.4.2.2 Installation from CD-ROM
- ACUCOBOL-GT Language Skeleton
- ACUCOBOL-GT Language Skeleton
- ACUCOBOL-GT Library Routines
- ACUCOBOL-GT Library Routines
- ACUCOBOL-GT, extensions to COBOL
- B.2 Extensions
- ACUCOBOL-GT, limits and ranges
- B.1 Limits and Ranges
- ACUCOBOL-GT, special features
- D.1 Introduction
- ACUCOBOL-GT, specifications
- B.1 Limits and Ranges
- ACUCOBOL-GT:restrictions
- B.3 Restrictions
- acugui.def
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- 4.2 Events
- W$MOUSE Routine
- W$BITMAP Routine
- AcuODBC
- 1.1 Product Overview
- AcuServer
- 5.2 AcuServer
- AcuServer requirements
- 5.2.1 System Requirements
- AcuServer with transaction management
- 5.1.10.1 Transaction logging and recovery with AcuServer
- acushare Utility Program
- 2.12 acushare Utility Program
- acushare, increasing the wait time
- 2.12.3.1 Runtime handling of errors
- acushare, indicating programs to share
- 2.12.2.1 Indicating programs to share
- acushare, kill
- 2.12.3 Starting and using acushare
- acushare, runtime errors
- 2.12.3.1 Runtime handling of errors
- acushare, starting
- 2.12.3 Starting and using acushare
- ACUSHARE_TIMEOUT environment variable
- 2.12.3.1 Runtime handling of errors
- ADD
- ADD
- 6.4.1 Arithmetic Operations
- ADD Statement
- ADD Statement
- ADD, CORRESPONDING option
- 6.4.5 CORRESPONDING Option
- ADD, general format
- ADD Statement
- ADD, syntax rules
- ADD Statement
- addition
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- addresses, specifying and debugger
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- ADVANCING, WRITE with
- WRITE Statement
- AFTER procedure, in the Screen Section
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- alfred color configuration variables
- 3.5.6 Configuration variables
- alfred error message file
- 3.5.3 Translation of Messages
- alfred indexed file record editor
- 3.5 Acucorp's Indexed File Record Editor-alfred
- alfred, editing records
- 3.5.5 Editing records
- alfred, limit on alternate keys
- 3.5.1 Modes of Operation
- alfred, modes of operation
- 3.5.1 Modes of Operation
- alfred, security
- 3.5.2 Security
- alfred, starting
- 3.5.4 Starting alfred
- ALFRED-. . .-BITMAP
- ALFRED-. . .-BITMAP
- ALFRED-. . .-COLOR
- ALFRED-. . .-COLOR
- ALFRED-BITMAP-FILE
- 3.5.6 Configuration variables
- ALFRED-BITMAP-FILE
- ALFRED-ENTRY-FIELDS
- ALFRED-ENTRY-FIELDS
- ALFRED-ENTRY-FIELDS, configuration variable
- 3.5.6 Configuration variables
- ALFRED-GET-PRINTER
- ALFRED-GET-PRINTER
- ALFRED-MESSAGE-FILE
- ALFRED-MESSAGE-FILE
- ALFRED-MESSAGE-FILE, configuration variable
- 3.5.6 Configuration variables
- ALFRED-PRINTER-NAME
- ALFRED-PRINTER-NAME
- ALFRED-PRINT-HEADER-n
- ALFRED-PRINT-HEADER-n
- ALFRED-TOOLS-FILE
- ALFRED-TOOLS-FILE
- ALFRED-TOOLS-FILE, configuration variable
- 3.5.6 Configuration variables
- alias for file name
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- A-LICENSE-RETRIES
- A-LICENSE-RETRIES
- alignment rules
- 5.1.4 Standard Alignment Rules
- ALL
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- ALL literal
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- ALL, and figurative constants
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- ALLOWING ALL
- OPEN Statement
- ALLOWING NO OTHERS
- OPEN Statement
- ALLOW-LEFT-DOUBLE
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-LEFT-DOWN
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-LEFT-UP
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-MIDDLE-DOUBLE
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-MIDDLE-DOWN
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-MIDDLE-UP
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-MOUSE-MOVE
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-RIGHT-DOUBLE
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-RIGHT-DOWN
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALLOW-RIGHT-UP
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- ALPHA directive
- 5.3.3.1 Alpha Directive
- alphabet, CODE-SET
- 5.4.9 CODE-SET Clause
- alphabet,specifying for sorting
- 4.1.2 Object-Computer Paragraph
- alphabetic
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- ALPHABETIC condition
- 6.3.2 Class Condition
- ALPHABETIC-LOWER condition
- 6.3.2 Class Condition
- ALPHABETIC-UPPER condition
- 6.3.2 Class Condition
- alphanumeric
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- alphanumeric edited
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- alphanumeric literals
- 2.1.2.2 Nonnumeric literals
- ALPHA-UPDATES keyword
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- ALTER
- ALTER
- ALTER Statement
- ALTER Statement
- ALTER, general format
- ALTER Statement
- alternate keys, limit with alfred
- 3.5.1 Modes of Operation
- ALTERNATE, FRAME style
- 5.10 Frame
- AND
- 6.3.6 Complex Conditions
- AND operation
- CBL_AND Routine
- ANSI COBOL, specifications
- B.1 Limits and Ranges
- ANSI DISPLAY, guidelines
- DISPLAY src-item (ANSI format)
- ANSI format
- 2.4 Source Formats
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- ANSI source, compiler option
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- ANSI standard
- 1.2 Acknowledgment
- ANSI X3.23-1985
- B.1 Limits and Ranges
- ANSI, ACCEPT and DISPLAY
- 2.3.1 ANSI ACCEPT and DISPLAY Verbs
- ANSI, compiler option
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- ANSI, source program format
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- ANSI-compliant directive
- 5.3.3 Syntax
- ANY THREAD
- WAIT Statement
- Appendices
- 1.2.4 Appendices
- Appendices, summary of contents
- 1.2.4 Appendices
- APPLY clause
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- APPLY-CODE-PATH
- APPLY-CODE-PATH
- APPLY-FILE-PATH
- APPLY-FILE-PATH
- Area A
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- Area B
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- A-RETRY-DELAY
- A-RETRY-DELAY
- arithmetic expression, and floating-point data
- 5.1.8.1 Using floating-point data
- arithmetic expressions
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- arithmetic operators
- 6.4.1 Arithmetic Operations
- ASCENDING, in SORT
- SORT Statement
- ASCII to Hexadecimal Conversion
- ASCII2HEX Routine
- ASCII to Octal Conversion
- ASCII2OCTAL Routine
- Asian character sets
- 4.4.4 Double-Byte Character Handling
- Assembly Language Interface
- Assembly Language Interface
- assembly routines, and Windows
- M.2.5 Differences between MS-DOS and Windows
- ASSIGN
- 2.8.2 File Name Examples
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- Assigning Files to Local Printers
- 2.8.3 Assigning Files to Local Printers
- AT END phrase
- 6.4.8 AT END and INVALID KEY Phrases
- AT phrase
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- AT, DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- AT, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- AT, line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- at-end condition
- 6.4.8 AT END and INVALID KEY Phrases
- audio file support (.WAV)
- WIN$PLAYSOUND Routine
- AUTO phrase
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- auto step
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- AUTO-BUFFER
- AUTO-BUFFER
- automatic mouse handling
- 7.4 Automatic Mouse Handling
- automatic synchronization
- C.4 Matching C Data Items
- automatic trailing space removal
- READ Statement
- STRIP-TRAILING-SPACES
- Automation Server
- M.3.6 Calling ACUCOBOL-GT From Other Programming Languages
- AUTO-MOUSE-HANDLING
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- AUTO-PROMPT
- AUTO-PROMPT
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- AUTO-RETURN keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- AUTO-SPIN style
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- A-WAIT-FOR-LICENSE
- A-WAIT-FOR-LICENSE
B
- background brush
- 9.9.1 Background Brush Color
- USE-MOUSE
- WHITE-FILL
- background color, color mapping
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- BACKGROUND-HIGH, LOW, and STANDARD
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- BACKGROUND-INTENSITY
- Step 2 - Assign Initial Attributes
- BACKGROUND-INTENSITY
- Color Configuration
- backup, vio archive utility
- 3.4 File Transfer Utility-vio
- BAR special properties:SHADING
- 5.11 Bar
- bars, vertical bars in manual
- 1.1.3 Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- 1.6 Notation
- BELL
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- BELL
- BINARY directive
- 5.3.3.2 Binary Directive
- binary sequential file, creating an indexed file from
- 3.3.8 Loading a File
- binary sequential files, and block size
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- binary sequential files, uploading from Vision files to
- 3.3.7 Unloading to Binary and Line Sequential Format
- binary sequential records
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- bitmap buttons
- 3.8 Bitmap Buttons
- bitmap buttons:color mapping
- 3.8.1 Drawing the Image
- bitmap buttons:creating in the Screen Section
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- bitmap buttons:creating the button
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- bitmap buttons:creating the image
- 3.8.1 Drawing the Image
- bitmap buttons:file format
- 3.8.1 Drawing the Image
- bitmap buttons:loading a bitmap
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- bitmap buttons:pop-up hints
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- bitmap buttons:pop-up hints:configuration variables
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- bitmap buttons:portability issues
- 3.8.5 Portability
- bitmap buttons:removing an image
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- bitmap buttons:size of image
- 3.8.1 Drawing the Image
- bitmap buttons:styles
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- bitmap buttons:W$BITMAP library routine
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- BITMAP control
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP, CHECK-BOX style
- 5.6 Check-Box
- BITMAP, RADIO-BUTTON style
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- BITMAP, style
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- BITMAP:common properties
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP:special properties
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP:special properties:BITMAP-HANDLE
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP:special properties:BITMAP-NUMBER
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP-HANDLE, BITMAP special property
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP-HANDLE, special property
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- BITMAP-HANDLE, TAB-CONTROL special property
- 5.13 Tab
- BITMAP-NUMBER, BITMAP special property
- 5.14 Bitmap
- BITMAP-NUMBER, TAB special property
- 5.13 Tab
- BITMAP-WIDTH, TAB special property
- 5.13 Tab
- bitmapped graphics in Windows
- W$BITMAP Routine
- blank line
- 2.2.4 Blank Lines and Comment Lines
- BLANK SCREEN
- 5.2 Global Styles
- BLANK WHEN ZERO clause, general format
- 5.7.1.13 BLANK WHEN ZERO clause
- BLINK, not supported
- 11.1.4 Regarding Configuration Variables
- BLOCK CONTAINS
- 5.4.4 BLOCK CONTAINS Clause
- block size, Vision files
- 5.4.4 BLOCK CONTAINS Clause
- blocking
- 5.4.4 BLOCK CONTAINS Clause
- blocking factor, setting
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- blocking-count, menu
- W$MENU Routine
- BOXED style:incompatible with menus
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- BOXED, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- BOXED, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- BOXED-FLOATING-WINDOWS
- BOXED-FLOATING-WINDOWS
- braces
- Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- 1.1.3 Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- brackets
- 1.1.3 Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- breakpoint
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- breakpoints
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- browser, displaying a message in status bar
- W$STATUS Routine
- browser, passing a URL to
- W$GETURL Routine
- BTRV-MASS-UPDATE
- BTRV-MASS-UPDATE
- BUFFERED-SCREEN
- BUFFERED-SCREEN
- buffers, V-Buffers
- V-BUFFERS
- BUTTONS, TAB style
- 5.13 Tab
C
- C subroutines: machine specific considerations for the runtime
- C.5 Creating a New Runtime System
- C subroutines:calling COBOL routines from C
- C.6 Calling COBOL Routines from C
- C subroutines:creating a new runtime system
- C.5 Creating a New Runtime System
- C subroutines:data types
- C.3.2 The "SUB85" Interface
- C subroutines:direct method of linking
- C.2 Direct Method
- C subroutines:interface method of linking
- C.3 Interface Method
- C subroutines:software required
- C.1 Overview of Interface Methods
- C subroutines:SUB interface
- C.3.1 The "SUB" Interface
- C subroutines:SUB85 interface
- C.3.2 The "SUB85" Interface
- C subroutines:using the Windows SDK
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- C$CALLEDBY Routine
- C$CALLEDBY Routine
- C$CALLERR Routine
- C$CALLERR Routine
- C$CHAIN Routine
- C$CHAIN Routine
- C$CHAIN routine, and installation on MS-DOS or OS/2
- A.3.1 Installation Steps
- C$CHAIN, and 32-bit Windows
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- C$CHAIN, how to return after a
- C$CHAIN Routine
- C$CHAIN, MS-DOS version
- C$CHAIN Routine
- C$CHDIR Routine
- C$CHDIR Routine
- C$CHDIR:using CODE-PREFIX with
- C$CHDIR Routine
- C$COPY Routine
- C$COPY Routine
- C$DELETE Routine
- C$DELETE Routine
- C$FILEINFO Routine
- C$FILEINFO Routine
- C$FILESYS Routine
- C$FILESYS Routine
- C$FULLNAME
- C$FULLNAME Routine
- C$GETCGI Routine
- C$GETCGI Routine
- C$JUSTIFY Routine
- C$JUSTIFY Routine
- C$KEYMAP Routine
- C$KEYMAP Routine
- C$LOCALPRINT Routine
- C$LOCALPRINT Routine
- C$LOCKPID Routine
- C$LOCKPID Routine
- C$MAKEDIR Routine
- C$MAKEDIR Routine
- C$MEMCPY (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- C$MEMCPY (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- C$NARG Routine
- C$NARG Routine
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- C$PARAMSIZE Routine
- C$PARAMSIZE Routine
- C$RECOVER Routine
- C$RECOVER Routine
- 5.1.10 Recovery
- C$RERR library routine
- C$RERR Routine
- C$RERRNAME Routine
- C$RERRNAME Routine
- C$RUN Routine
- C$RUN Routine
- C$SLEEP Routine
- C$SLEEP Routine
- C$SYSTEM Routine
- C$SYSTEM Routine
- C$TOLOWER
- C$TOUPPER and C$TOLOWER Routines
- C$TOUPPER
- C$TOUPPER and C$TOLOWER Routines
- C, alignment boundaries, and different C compilers
- C.4 Matching C Data Items
- C, and USAGE types for integer data
- C.4 Matching C Data Items
- C, compilers and alignment boundaries
- C.4 Matching C Data Items
- cache setting for HTML output from CGI programs
- CGI-NO-CACHE
- CALL
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- 3.2.1 Object Libraries
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- CALL
- EXIT Statement
- CALL RUN, memory considerations
- CALL Statement
- CALL Statement
- CALL Statement
- CALL THREAD
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- CALL verb, error messages
- C$CALLERR Routine
- CALL verb, library routines
- ACUCOBOL-GT Library Routines
- CALL, and runcbl steps
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- CALL, general format
- CALL Statement
- CALL, how to return after a C$CHAIN
- C$CHAIN Routine
- CALL, syntax rules
- CALL Statement
- called programs, passing parameters
- CALL Statement
- calling COBOL routines from C
- C.6 Calling COBOL Routines from C
- calling COBOL routines from other programming languages
- M.3.6 Calling ACUCOBOL-GT From Other Programming Languages
- calling program, Linkage Section
- 5.6 LINKAGE Section
- Calling Subprograms
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- CANCEL
- CALL Statement
- CANCEL
- 6.3 Memory Management
- 3.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- CANCEL ALL
- 6.3 Memory Management
- CANCEL Statement
- CANCEL Statement
- CANCEL, and runcbl steps
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- CANCEL, general format
- CANCEL Statement
- CAPTURE-MOUSE
- 3.7 Controls and the Mouse
- W$MOUSE Routine
- Carriage return doesn't advance cursor to next field
- 11.1.4 Regarding Configuration Variables
- CARRIAGE-CONTROL-FILTER
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- CARRIAGE-CONTROL-FILTER
- CASE keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- case, converting with library routine
- C$TOUPPER and C$TOLOWER Routines
- Case, lower/upper in command line
- 2.1.10 Upper and Lower Case
- case, of words in manual
- 1.1.1 Upper-Case and Special-Character Words
- case, Upper-Lower-Map
- UPPER-LOWER-MAP
- catastrophic exit
- 6.7 Exiting from ACUCOBOL-GT Programs
- CBL_AND Routine
- CBL_AND Routine
- CBL_COPY_FILE Routine
- CBL_COPY_FILE Routine
- CBL_CREATE_DIR Routine
- CBL_CREATE_DIR Routine
- CBL_DELETE_DIR Routine
- CBL_DELETE_DIR Routine
- CBL_DELETE_FILE Routine
- CBL_DELETE_FILE Routine
- CBL_EQ Routine
- CBL_EQ Routine
- CBL_NOT Routine
- CBL_NOT Routine
- CBL_OR Routine
- CBL_OR Routine
- CBL_XOR Routine
- CBL_XOR Routine
- cblconfig
- 1.1 Product Overview
- CBLFLAGS Environment Variable
- 2.1.13 CBLFLAGS Environment Variable
- cblutil program
- 3.2.2 Creating Object Libraries
- cblutil program, object file information command
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- cblutil program, object library options
- 3.2.2 Creating Object Libraries
- cblutil program,object information
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- CCOL, character coordinate phrase explained
- 3.6 The Character Coordinate Phrases
- cell grid, displaying in a window (debugging aid)
- WIN3-GRID
- CELL phrase
- 4.5.3 Coordinate Space Solutions
- CELL size, establishing in the main application window
- 1.6.3 Tips for Solving Cross Platform Interface Problems
- cell, defined
- 4.5.1 Coordinate Handling
- CELLS phrase, used with the character coordinate phrases
- 3.6 The Character Coordinate Phrases
- centering data with C$JUSTIFY
- C$JUSTIFY Routine
- CGI programs, merging data with HTML templates
- DISPLAY external-form-item
- CGI variables, how to retrieve
- C$GETCGI Routine
- CGI, retrieving a CGI variable
- 5.7.1.6 IS EXTERNAL-FORM clause
- CGI, setting the HTML output cache option
- CGI-NO-CACHE
- CGI-AUTO-HEADER
- CGI-AUTO-HEADER
- CGI-NO-CACHE
- CGI-NO-CACHE
- CHAIN
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- CHAIN
- CHAIN Statement
- CHAIN Statement
- CHAIN, general format
- CHAIN Statement
- CHAINING phrase
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- CHAIN-MENUS
- CHAIN-MENUS
- changes affecting Version 1.3
- Changes Affecting Version 1.3
- changes affecting Version 1.4
- Changes Affecting Version 1.4
- changes affecting Version 1.5
- Changes Affecting Version 1.5
- changes affecting Version 2.0
- Changes Affecting Version 2.0
- changes affecting Version 2.1
- Changes Affecting Version 2.1
- changes affecting Version 2.3
- Changes Affecting Version 2.3
- changes affecting Version 2.4
- Changes Affecting Version 2.4
- changes affecting Version 3.2
- Changes Affecting Version 3.2
- changes affecting Version 4.0
- Changes Affecting Version 4.0
- changes affecting Version 4.1
- Changes Affecting Version 4.1
- changes affecting Version 4.2
- Changes Affecting Version 4.2
- changing a menu item
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- character coordinate phrases
- 3.6 The Character Coordinate Phrases
- CHARACTER, label in Screen Section
- 4.3 Graphical vs. Textual Modes
- character-based emulation of windows and controls
- 4.6.7 Graphical Window and Control Emulation
- character-based, differences from graphical
- 1.6.1 Incompatibilities between Graphical and Character Systems
- characters, double-byte
- 4.4.4 Double-Byte Character Handling
- check marks on menus
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- W$MENU Routine
- check marks, adding and removing in menus dynamically
- 8.8.2 Checking Menu Items
- check marks, in menus
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- CHECK-BOX control
- 5.6 Check-Box
- CHECK-BOX:bitmap button, introduced
- 3.8 Bitmap Buttons
- CHECK-BOX:common properties
- 5.6 Check-Box
- CHECK-BOX:special properties
- 5.6 Check-Box
- CHECK-BOX:styles
- 5.6 Check-Box
- CHECK-BOX:styles:FRAMED
- 5.6 Check-Box
- CHECK-NUMBERS keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- CHECK-NUMBERS=Validate
- 6.6 Data Validation
- CHECK-USING
- CHECK-USING
- child window
- 2.4 Parent and Child Windows
- C-ISAM files, converting with vutil
- 3.3.11 Converting C-ISAM Files
- C-ISAM, and C$COPY routine
- C$COPY Routine
- C-ISAM-COMPRESS-KEYS
- C-ISAM-COMPRESS-KEYS
- class condition
- 6.3.2 Class Condition
- class name
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- class-name condition
- 6.3.2 Class Condition
- clauses
- 2.5.1.4 Clauses and entries
- clear all menus
- W$MENU Routine
- CLOSE
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- CLOSE
- CLOSE file
- CLOSE Statement
- CLOSE WINDOW
- CLOSE Statement
- CLOSE, and record locking
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- CLOSE, general format
- CLOSE Statement
- Close, handling under Windows
- 8.13 System Menu "Close" Handling under Windows
- CLOSE-ON-EXIT
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- CLOSE-ON-EXIT
- closing the main application window
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- CMD events for controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- CMD-ACTIVATE
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- CMD-GOTO
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- CMD-HELP
- 10.3 The Help Processor
- CMD-TABCHANGED
- 6.6 Data Validation
- CMD-GOTO
- 6.6 Data Validation
- COBOL implementations
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
- COBOL language elements
- 2.1 Language Elements
- COBOL program elements
- 2.5.1 Program Elements
- COBOL standard
- 1.2 Acknowledgment
- COBOL words, defined
- 2.1.1 COBOL Words
- code and data file search paths
- 2.7.2 Code and Data File Search Paths
- code sharing
- 2.12.2 Using shared memory
- Code sharing on AOS/VS
- 2.12.2.2 Code sharing on AOS/VS
- CODE-CASE
- CODE-CASE
- CODE-MAPPING
- CODE-MAPPING
- CODE-PREFIX
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- CODE-PREFIX
- 2.7.2 Code and Data File Search Paths
- CODE-PREFIX, using with C$CHDIR
- C$CHDIR Routine
- CODE-SET
- 5.4.9 CODE-SET Clause
- CODE-SUFFIX
- CODE-SUFFIX
- CODE-SYSTEM
- CODE-SYSTEM
- CODE-SYSTEM configuration variable
- 4.4.4 Double-Byte Character Handling
- CODE-SYSTEM variable, table
- 4.4.4 Double-Byte Character Handling
- collating sequence
- 4.1.2 Object-Computer Paragraph
- color
- 4.6.4 Color
- Color Configuration
- Color Configuration
- color attributes, of menus
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- color map, and SET ENVIRONMENT
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- color mapping
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- color mapping, for a bitmap
- 3.8.1 Drawing the Image
- color models, explained
- 9.2.1 What Is a Color Model?
- color options under Windows and Windows NT
- 9.9 Miscellaneous Options under Windows and Windows NT
- color remapping, quick global color changes
- 9.1.1 Simplified Mapping Approach
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- color values, foreground and background settings
- 9.8 COLOR-TABLE Settings
- color values, list of
- 9.8 COLOR-TABLE Settings
- color values, numeric
- 9.8 COLOR-TABLE Settings
- color, adding to monochrome displays
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- color, configuration variables
- Color Configuration
- color, customization for graphical environments
- 9.1.2 Controlling the Color Mapping
- color, disabling on MS-DOS
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- COLOR, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- COLOR, in line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- color, inherited by a new window
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- color, remapping with configuration variables
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- color, setting foreground & background
- 4.6.4 Color
- color, when terminal can display only one color at a time
- 4.6.4 Color
- COLOR, with DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- COLOR-MAP
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- COLOR-MAP
- COLOR-MODEL
- 9.1.1 Simplified Mapping Approach
- COLOR-MODEL
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- COLOR-MODEL settings
- 9.2 COLOR-MODEL Settings
- COLOR-MODEL Settings 1 and 2
- 9.3 COLOR-MODEL Settings 1 and 2
- COLOR-MODEL Settings 3 and 4
- 9.4 COLOR-MODEL Settings 3 and 4
- COLOR-MODEL Settings 5 and 6
- 9.5 COLOR-MODEL Settings 5 and 6
- COLOR-MODEL Settings 7 and 8
- 9.6 COLOR-MODEL Settings 7 and 8
- COLOR-MODEL Settings 9 and 10
- 9.7 COLOR-MODEL Settings 9 and 10
- COLOR-MODEL, settings described
- 9.2.1 What Is a Color Model?
- colors on Windows and Windows NT machines
- W$PALETTE Routine
- COLORS, BAR special property
- 5.11 Bar
- COLOR-TABLE
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- COLOR-TABLE
- 9.1.2 Controlling the Color Mapping
- COLOR-TABLE Settings
- 9.8 COLOR-TABLE Settings
- COLOR-TABLE, specifying color changes
- 9.8 COLOR-TABLE Settings
- COLOR-TRANS
- Step 3 - Transform Colors
- COLOR-TRANS
- Color Configuration
- color-val, and table
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- 5.9.3 OCCURS Clause
- COLUMN Clause
- 5.9.5 COLUMN Clause
- COLUMN NUMBER, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- COLUMN, DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- COLUMN, line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- COLUMN-SEPARATION
- COLUMN-SEPARATION
- Combined Condition
- Combined Condition
- combined condition, language skeleton
- Combined Condition
- combined conditions
- 6.3.6.1 Combined conditions
- combined relation conditions, abbreviated
- 6.3.8 Abbreviated Combined Relation Conditions
- COMBO-BOX control
- 5.9 Combo Box
- COMBO-BOX:common properties
- 5.9 Combo Box
- COMBO-BOX:data limit
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- COMBO-BOX:last item in
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- COMBO-BOX:styles
- 5.9 Combo Box
- COMBO-BOX:styles:DROP-DOWN
- 5.9 Combo Box
- COMBO-BOX:styles:DROP-LIST
- 5.9 Combo Box
- COMBO-BOX:styles:STATIC-LIST
- 5.9 Combo Box
- command events for controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- command line argument
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- command line, DISPLAY UPON COMMAND-LINE
- DISPLAY UPON COMMAND LINE
- command, executing an operating system
- SYSTEM Routine
- command, executing operating system command from Windows
- C$RUN Routine
- commands, notation of
- 1.6 Notation
- Comment
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- COMMENT directive
- 5.3.3.3 Comment Directive
- comment line
- 2.2.4 Blank Lines and Comment Lines
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- comment-entry
- 2.1.5 Comment Entries
- COMMIT
- COMMIT
- COMMIT, general format
- COMMIT Statement
- COMMIT, implicit
- 5.1.3 Transaction Management Verbs
- Common Gateway Interface
- 5.7.1.6 IS EXTERNAL-FORM clause
- common properties of controls, overview
- 3.1 Overview
- common properties table
- 5.1.2 Common Properties Table
- common statement rules
- 6.4 Common Statement Rules
- comparison, of nonnumeric operands
- 6.3.1.2 Comparison of nonnumeric operands
- comparison, of numeric operands
- 6.3.1.1 Comparison of numeric operands
- compatibility modes
- 2.3 Compiler Compatibility Modes
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
- Compatibility Options
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- compatibility, and large data items
- 5.1.6 Large Data Handling
- compatibility, with earlier versions of the runtime and compiler
- F.2 Changes Affecting Version 3.1
- compatibility, with older versions of file system interfaces
- F.4 Changes Affecting Version 2.3
- Compilation Problems
- 1.7.1 Compilation Problems
- compile command, error output
- 1.7.1 Compilation Problems
- compile option, segmentation in source
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- compiler directing statements
- 2.5.1.5 Statements
- compiler error messages, list of
- N.1 Introduction
- compiler option, @ character in filenames
- 2.1.11 File Name Handling
- compiler option, abbreviation of filenames
- 2.1.11 File Name Handling
- compiler option, ACCEPT and DISPLAY video
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- compiler option, ANSI
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- compiler option, ANSI source
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- compiler option, array references test
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- compiler option, cross-reference listing
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- compiler option, data storage
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- compiler option, data storage default, ACUCOBOL-GT
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- compiler option, data storage, IBM
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- compiler option, data storage, Micro Focus
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- compiler option, data storage SIGN clause
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- compiler option, debugging lines
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- compiler option, error file
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- compiler option, exclude source lines
- 2.6 Source Code Control
- compiler option, ICOBOL compatibility
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- compiler option, include source
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- compiler option, include source lines
- 2.6 Source Code Control
- compiler option, low intensity
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- compiler option, object file name
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- compiler option, page length of listings
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- compiler option, print all warning messages
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- compiler option, RM/COBOL compatibility
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- compiler option, terminal source format
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- compiler option, transaction files
- 2.1.4 File Options
- compiler option, verbose
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- compiler option, video--treating as if CONVERT specified
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- compiler option, warning message suppression
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- compiler options used with transaction management
- 5.1.9 Compiler File Options
- compiler options, compatibility
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- compiler options, copybook list
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- compiler options, debugging
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- compiler options, introduction
- 2.1 Using the Compiler
- compiler options, list of standard
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- compiler options, listing information
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- compiler options, mapping
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- compiler options, reserved words list
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- compiler options, reserved words suppression
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- compiler options, source files
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- compiler options, Video
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- Compiler, examples of use
- 2.1.12 Examples
- compiler, using
- 2.1 Using the Compiler
- compiler,installation
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- Compiler-Directing Statements
- Compiler-Directing Statements
- compiler-directing statements, language skeleton
- Compiler-Directing Statements
- compiling under Windows
- A.4.3 Compiling under Windows
- complex conditions
- 6.3.6 Complex Conditions
- COMPRESS-FACTOR
- COMPRESS-FACTOR
- COMPRESS-FILES
- COMPRESS-FILES
- compression
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- compression factor, option to set
- 3.3.10 Converting RM/COBOL-85 Indexed Files
- 3.3.12 Converting Micro Focus Files
- compression, configuration file option
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- compression, using WITH COMPRESSION
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- COMPUTATIONAL
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-1
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-2
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-3
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-4
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-5
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-6
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-N
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTATIONAL-X
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- COMPUTE
- COMPUTE
- 6.4.1 Arithmetic Operations
- COMPUTE, general format
- COMPUTE Statement
- concatenation, of data items
- STRING Statement
- condition, order of evaluation
- 6.3.7 Order of Evaluation
- conditional delimited-scope statements
- 2.5.1.5 Statements
- conditional expressions
- 6.3 Conditional Expressions
- conditional statement
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- condition-name
- 6.3.4 Condition-Name Condition
- 5.2.4 Condition-Name (Level 88)
- 5.7.1.14 VALUE clause
- condition-variable
- 6.3.4 Condition-Name Condition
- SET Statement
- config85.c
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- configuration file
- 1.1 Product Overview
- configuration file, format of
- 2.7 Runtime Configuration
- configuration file, information
- 2.1.14 Help, Version Information, and Communication with C Programs
- configuration file, names
- 2.7 Runtime Configuration
- configuration file, rules
- 2.7 Runtime Configuration
- H.1 Introduction
- configuration file, specifying location on LANs
- A.3.2.3 Using A_CONFIG
- configuration file, versus user's environment
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- Configuration Section
- 4.1 Configuration Section
- configuration variables
- H.1 Introduction
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- 4.2.3 Step three- Configuration Variables
- configuration variables for display
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- configuration variables, alfred
- 3.5.6 Configuration variables
- configuration variables, questions
- 11.1.4 Regarding Configuration Variables
- configuration variables, runtime
- 2.7 Runtime Configuration
- configuration variables, SET statement
- SET Statement
- configuration, of terminals
- A.2 Configuring Your Terminals
- constants
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- context ID (Windows help)
- 10.4 Windows Help
- context-sensitive help, see help automation
- 10.0 Help Automation
- continuation lines
- 2.2.3 Line Continuation
- CONTINUE
- CONTINUE
- CONTINUE, general format
- CONTINUE Statement
- control components diagram
- 5.1.1 Control Components Diagram
- control events
- 6.2 Control Events
- CONTROL KEY clause
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- control properties and styles, making a list
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- CONTROL VALUE
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- control:global style:NO-TAB
- 5.2 Global Styles
- control-name, example of structure
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- controls and windows, interaction
- 3.3 Interaction between Controls and Windows
- controls, creating, modifying, inquiring, and destroying
- 3.4 Creating, Modifying, Inquiring, and Destroying Controls
- controls, entering data into
- 3.5 Entering Data into a Control
- controls, questions
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- controls: SCROLL-BAR
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- controls:activating
- 3.5 Entering Data into a Control
- controls:BAR
- 5.11 Bar
- controls:basic components
- 3.1 Overview
- controls:BITMAP
- 5.14 Bitmap
- controls:CELLS phrase
- 3.6 The Character Coordinate Phrases
- controls:changing with the MODIFY statement
- MODIFY Statement
- controls:character-based emulation: default characters
- 4.6.7 Graphical Window and Control Emulation
- controls:common properties table
- 5.1.2 Common Properties Table
- controls:common properties, introduced
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- controls:common properties:introduced
- 3.1 Overview
- controls:compatibility with subwindows
- 3.3 Interaction between Controls and Windows
- controls:components of, overview
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- controls:constant ID
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- controls:emulation on character-based systems
- 4.6.7 Graphical Window and Control Emulation
- controls:handles
- 3.2 Control Types, Handles, and IDs
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- controls:identifier (ID)
- 3.2 Control Types, Handles, and IDs
- controls:interaction with subwindows
- DISPLAY control-type-name
- controls:list box:paged, search box
- 3.9.3 Other List Box Operations
- controls:LIST-BOX, PAGED
- 3.9 Paged List Boxes
- controls:LIST-BOX, PAGED: adding records to
- 3.9.2 Adding Records to a Paged List Box
- controls:LIST-BOX, PAGED: code example
- 3.9.5 Paged List Box Example
- controls:LIST-BOX, PAGED: event handling
- 3.9.4 Paged List Box Event Handling
- controls:mouse interaction
- 3.7 Controls and the Mouse
- controls:overview
- 3.1 Overview
- controls:PAGED LIST-BOX
- 3.9 Paged List Boxes
- controls:PAGED LIST-BOX: adding records to
- 3.9.2 Adding Records to a Paged List Box
- controls:PAGED LIST-BOX: code example
- 3.9.5 Paged List Box Example
- controls:PAGED LIST-BOX: event handling
- 3.9.4 Paged List Box Event Handling
- controls:positioning with character coordinate phrases
- 3.6 The Character Coordinate Phrases
- controls:positioning with the AT phrase
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- controls:properties, introduced
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- controls:removing runtime support for
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- controls:removing with DESTROY
- DESTROY Statement
- controls:retrieving information about
- INQUIRE Statement
- controls:screen repainting with WIN3-CLIP-CONTROLS
- WIN3-CLIP-CONTROLS
- controls:setting the background intensity
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- controls:size differences between graphical and text-mode systems
- 1.6.1 Incompatibilities between Graphical and Character Systems
- controls:special properties table
- 5.1.4 Special Properties Table
- controls:styles table
- 5.1.3 Styles Table
- controls:styles, introduced
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- controls:TAB
- 5.13 Tab
- controls:TEMPORARY-CONTROLS configuration file entry
- TEMPORARY-CONTROLS
- controls:text-mode:ACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR configuration variable
- ACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR
- controls:text-mode:GUI-CHARS configuration variable
- GUI-CHARS
- controls:text-mode:INACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR configuration variable
- INACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR
- controls:text-mode:MESSAGE-BOX-COLOR configuration variable
- MESSAGE-BOX-COLOR
- controls:text-mode:PROMPTING configuration variable
- PROMPTING
- controls:text-mode:RESIZE-FRAMES configuration variable
- RESIZE-FRAMES
- controls:text-mode:SHUTDOWN-MESSAGE-BOX configuration variable
- SHUTDOWN-MESSAGE-BOX
- controls:TREE-VIEW
- 5.16 Tree-View
- controls:types
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- 3.2 Control Types, Handles, and IDs
- conventions used in Reference Manual
- 1.1 Conventions Used in this Manual
- CONVERT, and compiler/video option
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- Converting C-ISAM Files
- 3.3.11 Converting C-ISAM Files
- Converting Micro Focus Files
- 3.3.12 Converting Micro Focus Files
- converting RM/COBOL data files
- 6.1.7 Converting RM/COBOL Data Files
- Converting RM/COBOL-85 Indexed Files
- 3.3.10 Converting RM/COBOL-85 Indexed Files
- converting text-based programs, dealing with coordinates
- 4.5 Coordinates
- converting, character to numeric value
- MOVE Statement
- CONVERTING, INSPECT with
- INSPECT Statement
- CONVERT-OUTPUT keyword
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- coordinate handling
- 4.5.1 Coordinate Handling
- coordinate space problems
- 4.5.2 Coordinate Space Problems
- coordinate space solutions
- 4.5.3 Coordinate Space Solutions
- coordinates
- 4.5 Coordinates
- coordinates, to position controls
- 4.5 Coordinates
- Copy Libraries
- 2.5 Copy Libraries
- COPY REPLACING with XFDs
- 5.3 XFD Files
- COPY statement, code examples
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- COPY, comparison operation
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- COPY, syntax and general rules
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- copybooks, list of all
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- copying a file, with C$COPY
- C$COPY Routine
- COPYPATH
- 2.5 Copy Libraries
- CORRESPONDING phrase
- 6.4.5 CORRESPONDING Option
- CORRESPONDING, MOVE with
- MOVE Statement
- Creating Empty Files
- 3.3.6 Creating Empty Files
- creating menu bars and pop-up menus
- 8.0 Creating Menu Bars and Pop-Up Menus
- Creating Object Libraries
- 3.2.2 Creating Object Libraries
- creating, modifying, inquiring, and destroying controls
- 3.4 Creating, Modifying, Inquiring, and Destroying Controls
- cross platform interface problems
- 1.6.3 Tips for Solving Cross Platform Interface Problems
- cross-reference listing
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- CURRENCY
- CURRENCY
- current window
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- Cursor and Mouse Handling in Source-Level Debugging
- 3.1.2 Cursor and Mouse Handling in Source-Level Debugging
- CURSOR phrase
- ACCEPT Statement
- cursor, position within field by mouse
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- cursor:position after DISPLAY control-type statement
- DISPLAY control-type-name
- CURSOR-MODE
- CURSOR-MODE
- CURSOR-PAST-END keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- CURSOR-TYPE
- CURSOR-TYPE
- cut/copy/paste for entry fields
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- cut/copy/paste via SET format 13
- SET Statement
D
- DASHED, BAR style
- 5.11 Bar
- data classes of
- 5.1.3 Classes of Data
- Data Description Entry
- Data Description Entry
- data description entry, general format
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- data description entry, level-numbers
- 5.7.1.1 Level-number
- data description entry, syntax rules
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- data dictionaries
- 5.3 XFD Files
- data dictionary file name
- 5.3.3.5 File Directive
- Data Division
- 5.0 Data Division
- Data Division
- Data Division, general format and rules
- 5.3 Data Division Format
- Data General
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
- Data General AOS/VS, installation
- A.7 Data General AOS/VS Machines
- data item, declaring external
- 5.7.1.4 IS EXTERNAL clause
- data items, constraints on large
- 5.1.6 Large Data Handling
- data items, format
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- data names, described
- 5.2 Data Names
- data names, qualification
- 5.2.1 Qualification
- data names, subscripting
- 5.2.2 Subscripting
- DATA RECORDS, general format
- 5.4.10 DATA RECORDS Clause
- data sharing among threads
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- Data Storage Options
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- Data Structures
- 5.1 Data Structures
- data types, and alignment
- 5.1.4 Standard Alignment Rules
- data validation
- 6.6 Data Validation
- data validation, not performed when
- 6.6 Data Validation
- data, categories of
- 5.1.3 Classes of Data
- data, external
- 5.5 WORKING-STORAGE Section
- data, large
- 5.1.6 Large Data Handling
- data, limits
- 5.1.6 Large Data Handling
- DATA-RANGE keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- DATE directive
- 5.3.3.4 Date Directive
- debugger commands
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- Debugger Restrictions
- 3.1.7 Debugger Restrictions
- debugger scroll bar
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- debugger, entering
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- debugger, example
- 1.7.2 Program Execution Problems
- debugger, file tracing option
- 3.1.4 File Tracing
- debugger, introduction
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- debugger, macros
- 3.1.5 Macro Debugger
- debugger, running the under Windows
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- debugger, specifying addresses
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- debugger, specifying program addresses
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- debugger, specifying variables
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- debugger, three modes
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- debugger, using mouse with
- 3.1.2 Cursor and Mouse Handling in Source-Level Debugging
- debugger: name qualification
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- debugging line
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- debugging lines
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- debugging lines, conditional in source
- 4.1.1 Source-Computer Paragraph
- debugging window
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- debugging:displaying a character cell grid
- WIN3-GRID
- debugging:setting a break point
- 11.1.5 Regarding Debugging
- DECIMAL-POINT
- DECIMAL-POINT
- Declarative
- 6.1.2 Flow of Control
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- 6.4.8 AT END and INVALID KEY Phrases
- declarative paragraphs
- 6.1 Organization
- DEFAULT-BUTTON, PUSH-BUTTON style
- 5.5 Push-Button
- DEFAULT-COUNT
- DEFAULT-COUNT
- DEFAULT-FONT
- DEFAULT-FONT
- DEFAULT-HOST
- DEFAULT-HOST
- DEFAULT-PROGRAM
- DEFAULT-PROGRAM
- defaults used in XFD Files
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- defines, compilation switch
- 10.4 Windows Help
- definition (.def) files
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- delays, creating with C$SLEEP
- C$SLEEP Routine
- DELETE
- DELETE
- DELETE FILE
- DELETE Statement
- DELETE RECORD
- DELETE Statement
- DELETE, and record locking
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- DELETE, general format
- DELETE Statement
- deleting a menu item
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- DELIMITED phrase, with STRING
- STRING Statement
- delimited-scope statement
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- delimited-scope statements
- 6.1.1.1 Scope of statements
- DESCENDING, in SORT
- SORT Statement
- DESTROY
- DESTROY
- DESTROY, general format
- DESTROY Statement
- DESTROY:value
- F.2 Changes Affecting Version 3.1
- device locking
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- device locking under UNIX
- 6.1.5 Device Locking Under UNIX
- device names, file processing
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- device names, list of valid
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- device naming conventions
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- devices
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- Dialog Box:creating
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- dialog box:Windows Common Dialogs
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- direct.c
- 5.7.1.4 IS EXTERNAL clause
- directive syntax
- 5.3.3 Syntax
- directives
- 5.3.2 Using Directives
- directory, changing current with C$CHDIR
- C$CHDIR Routine
- directory, creating with C$MAKEDIR
- C$MAKEDIR Routine
- disabling a menu item
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- disabling a menu item at creation
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- disabling an entire menu
- W$MENU Routine
- disabling menu items dynamically
- 8.8.1 Disabling Menu Items
- disk space, required for installation
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- DISPLAY
- DISPLAY
- 5.9.1 PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- display attributes, order of precedence
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY Control-Type
- DISPLAY control-type-name
- DISPLAY external-form-item
- DISPLAY external-form-item
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- display interface
- 4.4 The Display Interface
- DISPLAY LINE
- DISPLAY LINE
- DISPLAY LINE, and terminal manager
- 6.2.2 Terminal Manager Restrictions
- DISPLAY MESSAGE BOX
- DISPLAY MESSAGE BOX
- DISPLAY SCREEN SIZE
- DISPLAY SCREEN SIZE
- DISPLAY SCREEN, column mode
- DISPLAY SCREEN SIZE
- DISPLAY screen-name
- DISPLAY screen-name
- DISPLAY src-item
- DISPLAY src-item
- DISPLAY src-item (ANSI format)
- DISPLAY src-item (ANSI format)
- DISPLAY Statement
- DISPLAY Statement
- DISPLAY SUBWINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- DISPLAY UPON COMMAND-LINE
- DISPLAY UPON COMMAND LINE
- DISPLAY UPON FLOATING WINDOW TITLE
- DISPLAY UPON GLOBAL TITLE
- DISPLAY UPON GLOBAL TITLE
- DISPLAY UPON GLOBAL TITLE
- DISPLAY UPON WINDOW TITLE
- DISPLAY UPON WINDOW TITLE
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY, and color
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- DISPLAY, ANSI
- DISPLAY src-item (ANSI format)
- display, configuring
- 4.4 The Display Interface
- DISPLAY, general format
- DISPLAY Statement
- DISPLAY, general rules
- DISPLAY src-item
- DISPLAY, screen options
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- DISPLAY, Screen Section
- DISPLAY screen-name
- DISPLAY, Screen Section and CONVERT-OUTPUT
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- DISPLAY, summary of different forms of
- DISPLAY Statement
- DISPLAY, syntax rules
- DISPLAY screen-name
- DISPLAY UPON WINDOW TITLE
- DISPLAY UPON COMMAND LINE
- DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- DISPLAY LINE
- DISPLAY src-item
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY src-item (ANSI format)
- DISPLAY SCREEN SIZE
- DISPLAY UPON GLOBAL TITLE
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- DISPLAY control-type-name
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- DISPLAY MESSAGE BOX
- DISPLAY external-form-item
- DISPLAY:DISPLAY SUBWINDOW statement:CONTROL VALUE phrase
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY-SWITCH-PERIOD
- DISPLAY-SWITCH-PERIOD
- 6.8.4 Thread Priorities
- DIVIDE
- DIVIDE
- DIVIDE Statement
- DIVIDE Statement
- division
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- division header
- 2.5.1.1 Division header
- DLL-CONVENTION
- DLL-CONVENTION
- DLLs
- M.2.4 Calling DLLs
- Document Overview
- 1.2 Document Overview
- DOS, differences from Windows
- M.2.5 Differences between MS-DOS and Windows
- DOS, differences with Windows NT
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- DOS-BOX-CHARS
- DOS-BOX-CHARS
- DOS-OUTPUT-METHOD
- DOS-OUTPUT-METHOD
- DOT-DASH, BAR style
- 5.11 Bar
- DOTTED, BAR style
- 5.11 Bar
- double-byte character handling
- 4.4.4 Double-Byte Character Handling
- DOUBLE-CLICK-TIME
- DOUBLE-CLICK-TIME
- DROP-DOWN, COMBO-BOX style
- 5.9 Combo Box
- DROP-LIST, COMBO-BOX style
- 5.9 Combo Box
- dynamic link libraries (DLLs), calling in Windows
- M.2.4 Calling DLLs
- dynamic memory, allocating
- M$ALLOC (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- dynamic memory, freeing previously allocated
- M$FREE (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- dynamic memory, retrieving data from allocated
- M$GET (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- dynamic memory, routines to handle
- Routines to Handle Dynamic Memory
- dynamic memory, storing data in allocated block
- M$PUT (Dynamic Memory Routine)
E
- EBCDIC,using this alphabet
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- EDITED-UPDATES keyword
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- editing records with alfred
- 3.5.5 Editing records
- editing, types allowed in PICTURE clause
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- EDIT-MODE
- EDIT-MODE
- EF-UPPER-WIDE
- EF-UPPER-WIDE
- EF-WIDE-SIZE
- EF-WIDE-SIZE
- elementary data item
- 5.1.1 Record Description
- elementary items, in data description entry
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- ellipses
- 1.1.4 Ellipses
- Ellipses
- e-mail, Acucorp
- 1.7 How To Get Help
- embedded procedures
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- 6.5.5 Using Screen Section Embedded Procedures
- emulation of graphical controls on character-based
- 4.6.7 Graphical Window and Control Emulation
- ENABLE-MOUSE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- encryption
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- Entering the Debugger
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- entry
- 2.5.1.4 Clauses and entries
- ENTRY-FIELD
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- ENTRY-FIELD control:setting the width
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- ENTRY-FIELD:common properties
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- ENTRY-FIELD:editing keys
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- ENTRY-FIELD:multiple lines
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- ENTRY-FIELD:size limit
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- environment
- SET Statement
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- Environment Division
- 4.0 Environment Division
- Environment Division
- Environment Division, language skeleton
- Environment Division
- environment variable, CBLFLAGS
- 2.1.13 CBLFLAGS Environment Variable
- environment variables
- 1.5 Environment Variables
- 1.1 Product Overview
- environment variables in the OF phrase of a COPY statement
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- environment variables to define a path
- 2.5 Copy Libraries
- environment variables, in the path-name
- 2.5 Copy Libraries
- EOF-ABORTS
- EOF-ABORTS
- EOL-CHAR
- EOL-CHAR
- EQUAL TO condition
- 6.3.1 Relation Conditions
- EQUALS operation
- CBL_EQ Routine
- ERASE, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- error 98 codes
- J.3 Vision Secondary Error Codes for Error 98s
- error code for W$MENU
- W$MENU Routine
- error codes for bitmapped graphics
- W$BITMAP Routine
- error codes for transactions
- J.4 Transaction Error Codes
- error codes, hardware errors under Windows
- M.2.5 Differences between MS-DOS and Windows
- error codes, primary errors for transactions
- J.4.1 Primary Error Codes
- error codes, secondary error codes for error 98's
- J.3 Vision Secondary Error Codes for Error 98s
- error codes, secondary errors for transactions
- J.4.2 Secondary Error Codes for Error 01
- error codes, Windows NT and hardware
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- error handling
- 6.4 Error Handling
- error handling, hardware
- WIN-ERROR-HANDLING
- error handling, hardware errors under Windows
- M.2.3 Hardware Error Handling
- error handling, hardware errors under Windows NT
- M.3.3 Hardware Error Handling
- error list for compiler
- N.2 List of Errors
- error messages, list of compiler error messages
- N.1 Introduction
- errors, acushare
- 2.12.3.1 Runtime handling of errors
- errors, logging to runtime's error file
- 6.4.2 Logging Errors to the Runtime's Error File
- ERRORS-OK
- ERRORS-OK
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- escape sequences, terminal manager restrictions
- 6.2.2 Terminal Manager Restrictions
- escape sequences, terminal manager solutions for
- 6.2.2 Terminal Manager Restrictions
- ESCAPE-BUTTON, PUSH-BUTTON style
- 5.5 Push-Button
- EVALUATE
- EVALUATE
- EVALUATE statement, code examples
- EVALUATE Statement
- EVALUATE statement, highlights for first-time users
- EVALUATE Statement
- EVALUATE, general format
- EVALUATE Statement
- EVALUATE, general rules
- EVALUATE Statement
- evaluation, order of
- 6.2.1 Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions
- event driven systems, described
- 1.2.1 Event-Driven Environments
- event procedure, in Screen Section
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- event procedure, modifying
- MODIFY Statement
- EVENT STATUS
- 4.2 Events
- 6.0 Events Reference
- 10.3 The Help Processor
- EVENT-DATA-2
- 10.3 The Help Processor
- events, described
- 6.0 Events Reference
- 4.2 Events
- events:controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- events:menus
- 6.3 Menu Events
- events:mouse, not returned as in Version 2.4
- 11.1.4 Regarding Configuration Variables
- events:Screen Section handling
- 6.0 Events Reference
- events:terminating, described
- 4.2 Events
- events:windows
- 6.1 Window Events
- event-status, example of structure
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- Examining File Information
- 3.3.1 Examining File Information
- example of menu handling
- 8.12 Menu Handling-Sample Code
- example using W$MENU
- 8.12 Menu Handling-Sample Code
- Examples
- 2.1.12 Examples
- EXCEPTION clause
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- exception keys
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- exception keys, and menus
- 8.6 Menu Input
- EXCEPTION procedure, in the Screen Section
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- EXCEPTION-RANGE keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- EXCEPTION-VALUE
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- Exclusive OR operation
- CBL_XOR Routine
- EXIT
- EXIT
- EXIT PARAGRAPH
- EXIT Statement
- EXIT PERFORM
- EXIT Statement
- EXIT Statement
- EXIT Statement
- EXIT-CURSOR
- EXIT-CURSOR
- exiting from ACUCOBOL-GT programs
- 6.7 Exiting from ACUCOBOL-GT Programs
- EXIT-STATUS
- SYSTEM Routine
- exponentiation
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- EXTEND-CREATES
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- EXTEND-CREATES
- extended file status
- C$RERR Routine
- extensions to COBOL
- B.2 Extensions
- external data item
- 5.5 WORKING-STORAGE Section
- 5.7.1.4 IS EXTERNAL clause
- external data items
- 6.3.1 External Data Items
- EXTERNAL data items, in Working-Storage
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- EXTERNAL data items, level-numbers
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- external files
- 5.4.1 File Description Entry
- 5.4.3 IS EXTERNAL Clause
- external name of file, VALUE OF FILE-ID
- 5.4.8 VALUE OF FILE-ID Clause
- EXTERNAL, general format
- 5.7.1.4 IS EXTERNAL clause
- EXTERNAL-FORM
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- EXTERNAL-FORM clause
- 5.7.1.6 IS EXTERNAL-FORM clause
- EXTERNAL-SIZE
- EXTERNAL-SIZE
- Extracting Records from a File
- 3.3.5 Extracting Records from a File
- EXTRA-KEYS-OK
- EXTRA-KEYS-OK
F
- F10-IS-MENU
- F10-IS-MENU
- FAQ
- 11.1 Frequently Asked Questions
- FAST-ESCAPE
- FAST-ESCAPE
- FIELDS-UNBOXED
- FIELDS-UNBOXED
- figurative constants
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- file attributes, and LAN installation
- A.3.2.2 Modifying File Attributes
- File Control Entry
- File Control Entry
- FILE CONTROL section
- 5.3 XFD Files
- file deletion with C$DELETE
- C$DELETE Routine
- File Description
- File Description
- file description entry
- 5.4.1 File Description Entry
- FILE directive
- 5.3.3.5 File Directive
- file extensions with SYSTEM calls
- SYSTEM Routine
- M.2.5 Differences between MS-DOS and Windows
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- file extensions, and execution under Windows
- A.4.4 Running your programs
- file handling
- 6.1 Handling Files
- File Handling Options
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- file information, retrieving with C$FILEINFO
- C$FILEINFO Routine
- file integrity
- 3.3.2 Testing File Integrity
- file locking, performance considerations
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- file locking, three forms
- OPEN Statement
- file name aliasing
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- file name assignments
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- File Name Examples
- 2.8.2 File Name Examples
- File Name Handling
- 2.1.11 File Name Handling
- File Name Interpretation
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- file names with embedded spaces
- FILENAME-SPACES
- file names, with hyphen
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- File Options
- 2.1.4 File Options
- file recovery with C$RECOVER
- 5.1.10 Recovery
- file recovery, library routine for
- C$RECOVER Routine
- file search routine to find full name
- C$FULLNAME Routine
- File Section, BLOCK CONTAINS
- 5.4.4 BLOCK CONTAINS Clause
- File Section, CODE-SET clause
- 5.4.9 CODE-SET Clause
- File Section, DATA RECORDS
- 5.4.10 DATA RECORDS Clause
- File Section, file description entry
- 5.4.1 File Description Entry
- File Section, general format
- 5.4 File Section
- File Section, IS EXTERNAL
- 5.4.3 IS EXTERNAL Clause
- File Section, LABEL RECORDS clause
- 5.4.6 LABEL RECORDS Clause
- File Section, LINAGE
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- File Section, RECORD clause
- 5.4.5 RECORD Clause
- File Section, sort file description entry
- 5.4.2 Sort File Description Entry
- file segment, setting with V-SEG-SIZE configuration variable
- V-SEG-SIZE
- File Size Summary Report
- 3.3.9 File Size Summary Report
- FILE STATUS
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- C$RERR Routine
- file status codes
- J.1 Introduction
- 2.7.3 File Status Codes
- file status codes, different standards (table)
- J.2 Table of Codes
- file status information, library routine for
- C$RERRNAME Routine
- C$RERR Routine
- FILE STATUS variable
- 6.4.7 I/O Status
- file system information, retrieving with C$FILESYS
- C$FILESYS Routine
- file trace , how to use
- 1.7.2 Program Execution Problems
- file tracing
- 3.1.4 File Tracing
- 3.1.4 File Tracing
- File Transfer Utility-vio
- 3.4 File Transfer Utility-vio
- file translation, examples of rules
- 2.8.2 File Name Examples
- file types, organization of
- 5.1.7 File Types
- file utilities, vutil
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
- File Utilities-vutil
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
- file, compression
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- file, copying with C$COPY
- C$COPY Routine
- file, encryption
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- file, vutil integrity check
- 3.3.2 Testing File Integrity
- FILE-CASE
- FILE-CASE
- FILE-CONDITION
- FILE-CONDITION
- FILE-CONTROL, general format
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- FILE-CONTROL, general rules
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- FILE-CONTROL, syntax rules
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- FILE-IO-PROCESSES-MESSAGES
- FILE-IO-PROCESSES-MESSAGES
- filename-HOST
- filename-HOST
- filename-LOG
- filename-LOG
- filenames, abbreviation when compiling
- 2.1.11 File Name Handling
- filenames, case of
- 2.1.10 Upper and Lower Case
- FILENAME-SPACES
- FILENAME-SPACES
- FILE-POS, GRID special property
- 5.15 Grid
- FILE-PREFIX
- 2.7.2 Code and Data File Search Paths
- FILE-PREFIX
- files, examining file information
- 3.3.1 Examining File Information
- files, improving performance
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- files, limits on open files and control of
- 6.1.9 Limits on Open Files
- files, rebuilding
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- files, reducing number of
- 3.2.1 Object Libraries
- files, reducing size of
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- files, sequential
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- files, sequential access
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- files, shared
- 5.4.3 IS EXTERNAL Clause
- files, when not in open mode
- 3.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
- FILE-STATUS-CODES
- FILE-STATUS-CODES
- 2.7.3 File Status Codes
- FILE-SUFFIX
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- FILE-SUFFIX
- filesystem-DETACH
- filesystem-DETACH
- FILLER
- 5.7.1.2 The data-name or FILLER clause
- FILLER data items and XFDs
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- find backwards
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- find forwards
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- find from top
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- floating window, inquiries
- 2.5 Creating, Inquiring, Modifying, and Destroying Windows
- floating window:ACCEPT statement, effects of
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- floating window:active
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- floating window:BOXED border
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- floating window:child
- 2.4 Parent and Child Windows
- floating window:closing
- 2.5 Creating, Inquiring, Modifying, and Destroying Windows
- floating window:closing with DESTROY
- DESTROY Statement
- floating window:closing:effect on current
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- floating window:creating
- 2.5 Creating, Inquiring, Modifying, and Destroying Windows
- floating window:current
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- floating window:defined
- 1.5 ACUCOBOL-GT Window Types
- floating window:getting the size and position of
- 2.5 Creating, Inquiring, Modifying, and Destroying Windows
- floating window:GRAPHICAL option
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- floating window:implicit subwindow
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- floating window:main application window, creating for optimal CELL size
- 1.6.3 Tips for Solving Cross Platform Interface Problems
- floating window:menu in
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- floating window:MODAL and MODELESS
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- floating window:modifying
- 2.5 Creating, Inquiring, Modifying, and Destroying Windows
- floating window:parent
- 2.4 Parent and Child Windows
- floating windows and subwindows, relationship
- 2.2 The Relationship Between Floating Windows and Subwindows
- floating windows, overview
- 2.1 Overview
- floating-point data, arithmetic expression
- 5.1.8.1 Using floating-point data
- floating-point data, differences from normal numeric
- 5.1.8 Floating-Point Data
- floating-point data, when to use
- 5.1.8 Floating-Point Data
- floating-point literals
- 2.1.2.1 Numeric literals
- flow of control
- 6.1.2 Flow of Control
- flush buffers, COMMIT
- COMMIT Statement
- FLUSH-ALL
- FLUSH-ALL
- FLUSH-COUNT
- FLUSH-COUNT
- FLUSH-ON-ACCEPT
- FLUSH-ON-ACCEPT
- FLUSH-ON-COMMIT
- FLUSH-ON-COMMIT
- FLUSH-ON-OPEN
- FLUSH-ON-OPEN
- FONT
- FONT
- font of window title
- WINDOW-TITLE
- font, condensed
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- font:measuring with W$TEXTSIZE
- W$TEXTSIZE Routine
- FONT-AUTO-ADJUST
- FONT-AUTO-ADJUST
- fonts, memory management of
- 4.6 Fonts
- fonts, support for
- 4.6 Fonts
- fonts.def
- W$FONT Routine
- fonts:selecting a custom font
- 11.1.3 Regarding Fonts
- fonts:selecting with W$FONT
- W$FONT Routine
- FONT-SIZE-ADJUST
- FONT-SIZE-ADJUST
- FONT-WIDE-SIZE-ADJUST
- FONT-WIDE-SIZE-ADJUST
- FOREGROUND-INTENSITY
- Color Configuration
- Step 2 - Assign Initial Attributes
- FOREGROUND-INTENSITY
- FOREGROUND-INTENSITY, configuration variable
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- format, of source code
- 2.4 Source Formats
- format, of source program
- 2.2 Source Format
- Formats for COBOL Verbs
- Formats for COBOL Verbs
- form-feeds
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- form-level ACCEPT and DISPLAY
- 6.5.4 Comparison to Field-level
- FRAME control
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAME:common properties
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAME:sizing problems
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- FRAME:styles
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAME:styles:ALTERNATE
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAME:styles:HEAVY
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAME:styles:RAISED
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAME:styles:VERY-HEAVY
- 5.10 Frame
- FRAMED, RADIO-BUTTON style
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- FRAMED, style
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- FULL
- 6.6 Data Validation
- FULL-BOXES
- FULL-BOXES
- function codes for terminals, list of
- 4.6 The Terminal Database File
- function key handling
- 8.6.1 Function Key Handling
- function keys, and menu bars
- 8.6.1 Function Key Handling
- function keys, defining
- 4.6.5 Function Keys and Other Keys
G
- genmenu, compiling the utility
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- GET-MOUSE-SCREEN-STATUS
- W$MOUSE Routine
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- GET-MOUSE-SHAPE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- GET-MOUSE-STATUS
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- W$MOUSE Routine
- GetStockObject, Windows API function
- 4.6 Fonts
- Getting Object Information
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- Getting Your Terminals Ready
- 4.2 Getting Your Terminals Ready
- GLOBAL, data description entry
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- go
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- GO TO
- GO TO
- GO TO, ALTER statement
- ALTER Statement
- GO TO, general format
- GO TO Statement
- GOBACK
- GOBACK
- GOBACK, general format
- GOBACK Statement
- graphical and textual modes, mixed
- 4.3 Graphical vs. Textual Modes
- graphical user interface, development strategies
- 1.6.2 Strategies for Supporting Multiple Systems
- graphical user interface, portability issues
- 1.6 Creating Portable User Interfaces
- graphical window and control emulation
- 4.6.7 Graphical Window and Control Emulation
- GRAPHICAL, label in Screen Section
- 4.3 Graphical vs. Textual Modes
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- Graphics Device Interface (GDI)
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- graphics on terminals requiring multiple-character escape sequences for line segments
- 4.6.6 Line Drawing
- graphics, bitmapped in Windows
- W$BITMAP Routine
- GREATER THAN condition
- 6.3.1 Relation Conditions
- grid control
- 5.15 Grid
- group item
- 5.1.1 Record Description
- group items
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- group items, category
- 5.1.3 Classes of Data
- GUI development project issues
- 1.7 GUI Development Project Issues
- GUI development with third party kits and tools
- 1.2.4 GUI Development with Third Party Kits and Tools
- GUI support, introduced
- 1.1 Overview of User Interface Features
- GUI-CHARS
- GUI-CHARS
H
- handle, described
- 4.1 Handles
- handle:invalid
- 4.1 Handles
- handle:POP-UP AREA phrase
- 4.1 Handles
- handles:control
- 3.2 Control Types, Handles, and IDs
- hardware and software requirements, Windows
- A.4.1 Hardware and software requirements
- hardware error handling, under Windows
- M.2.3 Hardware Error Handling
- hardware error handling, under Windows NT
- M.3.3 Hardware Error Handling
- hardware supported
- 1.4 Supported Hardware
- hardware type, and large data items
- 5.1.6 Large Data Handling
- HEAVY, FRAME style
- 5.10 Frame
- HEIGHT-IN-CELLS, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- help automation
- 10.1 HELP-ID
- help automation via SET format 13
- SET Statement
- help automation, mapping context IDs
- 2.1.14 Help, Version Information, and Communication with C Programs
- help automation:with MS Windows
- 10.4 Windows Help
- help command
- 2.1.14 Help, Version Information, and Communication with C Programs
- help compiler
- 10.4 Windows Help
- $WINHELP Routine
- HELP CONTENTS
- $WINHELP Routine
- help cursor
- 10.2 Help Modes
- HELP HELPONHELP
- $WINHELP Routine
- help key exception value
- 10.2 Help Modes
- help modes
- 10.2 Help Modes
- HELP PARTIALKEY
- $WINHELP Routine
- help processor
- 10.1 HELP-ID
- 10.3 The Help Processor
- HELP QUIT
- $WINHELP Routine
- help with debugger
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- help, how to get
- 1.7 How To Get Help
- Help, interfacing to the Windows facility
- $WINHELP Routine
- Help, Version Information, and Communication with C Programs
- 2.1.14 Help, Version Information, and Communication with C Programs
- HELP-CONTEXT
- 10.4 Windows Help
- HELP-CONTEXTPOPUP
- 10.4 Windows Help
- HELP-ID
- 10.1 HELP-ID
- HELP-PROGRAM, configuration variable
- 10.3 The Help Processor
- hex literals
- 2.1.2.2 Nonnumeric literals
- Hexadecimal to ASCII Conversion
- HEX2ASCII Routine
- Highlight item in debugger menu
- 3.1.2 Cursor and Mouse Handling in Source-Level Debugging
- HIGH-VALUES
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- HINTS-OFF
- HINTS-OFF
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- HINTS-ON
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- HINTS-ON
- HORIZONTAL, SCROLL-BAR style
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- HOT-KEY
- HOT-KEY
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- How the Terminal Manager Works
- 4.1 How the Terminal Manager Works
- How To Get Help
- 1.7 How To Get Help
- HP cartridge tapes
- A.5.1.2 HP cartridge tapes
- HP3000 Machines Running MPE/iX
- A.8 HP3000 Machines Running MPE/iX
- HTML output cache, setting this option
- CGI-NO-CACHE
- HTML templates, merging data with
- DISPLAY external-form-item
- HTML, associating group items with HTML data
- 5.7.1.6 IS EXTERNAL-FORM clause
- HTML, locating template files
- HTML-TEMPLATE-PREFIX
- HTML-TEMPLATE-PREFIX
- HTML-TEMPLATE-PREFIX
- hyphens, special treatment of file names with
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
I
- I/O efficiency
- 5.3.3.9 Use Group Directive
- I/O status
- 6.4.7 I/O Status
- ICOBOL
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- DISPLAY src-item
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
- 5.9.5 COLUMN Clause
- 5.7.1.11 SYNCHRONIZED clause
- ICOBOL compatibility
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- ICOBOL Conversion Guide
- K.1 Compile-Time Issues
- ICOBOL, ACUCOBOL-GT differences
- K.3 Differences
- ICOBOL, and file status codes
- 2.7.3 File Status Codes
- ICOBOL, compatibility mode
- 2.3 Compiler Compatibility Modes
- ICOBOL, compile-time issues
- K.1 Compile-Time Issues
- ICOBOL, conversion guide
- K.1 Compile-Time Issues
- ICOBOL, ERASE
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY src-item
- ICOBOL, file status codes
- J.1 Introduction
- ICOBOL, reserved words
- D.1 Introduction
- ICOBOL, reserved words option
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- ICOBOL, runtime options
- K.2 Runtime Options
- ICOBOL, terminal source format
- 2.4 Source Formats
- ICOBOL:ICOBOL-FILE-SEMANTICS configuration variable
- K.2 Runtime Options
- ICOBOL-FILE-SEMANTICS
- ICOBOL-FILE-SEMANTICS
- ICON
- ICON
- icon, using to execute program
- A.4.4 Running your programs
- ID, of a control
- 3.2 Control Types, Handles, and IDs
- Identification Division
- Identification Division
- 3.0 Identification Division
- Identification Division, language skeleton
- Identification Division
- IDENTIFIED
- 5.7.1 Data Description Entry
- IF
- IF
- IF, general format
- IF Statement
- imperative sentence
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- imperative statement
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- imperative statements
- 2.5.1.5 Statements
- IMPLIED-DECIMAL keyword
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- import screen facility
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- INACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR
- INACTIVE-BORDER-COLOR
- incompatibilities between graphical and character systems
- 1.6.1 Incompatibilities between Graphical and Character Systems
- index values, re-using
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- indexed file considerations
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- indexed file features
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- indexed file record editor, alfred
- 3.5 Acucorp's Indexed File Record Editor-alfred
- Indexed File Record Editor-alfred
- 3.5 Acucorp's Indexed File Record Editor-alfred
- indexed file utility
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
- indexed files
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- indexed files, organization of
- 5.1.7 File Types
- Indicating programs to share
- 2.12.2.1 Indicating programs to share
- indicator area
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- initial attribute
- CALL Statement
- EXIT Statement
- INITIAL PROGRAM
- 3.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
- 6.3 Memory Management
- initialization strings, for terminals
- 4.6.9 Initialization
- INITIALIZE
- INITIALIZE
- INITIALIZE, general format
- INITIALIZE Statement
- INPUT PROCEDURE
- SORT Statement
- input, simulating
- W$KEYBUF Routine
- INPUT-OUTPUT Section
- 4.2 Input-Output Section
- INPUT-STATUS-DEFAULT
- INPUT-STATUS-DEFAULT
- INQUIRE
- INQUIRE
- INQUIRE, general format
- INQUIRE Statement
- INSERTION-INDEX, use with PAGED list boxes
- 3.9.2 Adding Records to a Paged List Box
- INSERT-MODE
- INSERT-MODE
- INSERT-ROWS, GRID special property
- 5.15 Grid
- INSPECT
- INSPECT
- INSPECT statement, code examples
- INSPECT Statement
- INSPECT statement, general format
- INSPECT Statement
- INSPECT, comp-val and targ rules
- INSPECT Statement
- INSPECT, general rules
- INSPECT Statement
- installation from CD-ROM
- A.4.2.2 Installation from CD-ROM
- installation instructions
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- installation on MS-DOS and OS/2
- A.3 MS-DOS and OS/2 Machines
- installation on VMS and Open VMS
- A.6 VMS and Open VMS Machines
- installation procedure, for UNIX, Xenix, Ultrix and Unos
- A.5.1 Extracting the files
- installation under AOS/VS
- A.7 Data General AOS/VS Machines
- installation under Windows
- A.4 Windows Machines
- A.4.2 Installation steps for Windows
- installation under Windows, from diskette
- A.4.2.1 Installation from diskette
- installation, configuring terminals
- A.2 Configuring Your Terminals
- installation, MPE/iX
- A.8 HP3000 Machines Running MPE/iX
- installation, networks
- A.3.2 Network Environments
- installing on NeXT machines running UNIX
- A.5.3 Installing on NeXT Machines Running UNIX
- Internet, overview of options for deploying on the
- 6.9 Deploying Applications on the Internet
- 6.9.1 Options
- INTENSITY-FLAGS
- INTENSITY-FLAGS
- Color Configuration
- Step 4 - Transform Intensities
- Internet, defining records for HTML forms
- 5.7.1.6 IS EXTERNAL-FORM clause
- Internet, how to deploy applications on the
- 6.9 Deploying Applications on the Internet
- Internet, how to display a message in the browser status bar
- W$STATUS Routine
- Internet, how to retrieve CGI variables
- C$GETCGI Routine
- Internet, locating HTML template files
- HTML-TEMPLATE-PREFIX
- Internet, passing a URL to a browser
- W$GETURL Routine
- INVALID KEY phrase
- 6.4.8 AT END and INVALID KEY Phrases
- invalid-key condition
- 6.4.8 AT END and INVALID KEY Phrases
- IOBENCH.CBL
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- I-O Control Entry
- I-O Control Entry
- I-O-CONTROL, general format
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- I-O-CONTROL, general rules
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- I-O-CONTROL, syntax rules
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- IO-CREATES
- IO-CREATES
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- IO-READ-LOCK-TEST
- IO-READ-LOCK-TEST
- IS EXTERNAL
- 5.4.3 IS EXTERNAL Clause
- IS EXTERNAL, general format
- 5.7.1.4 IS EXTERNAL clause
- IS NUMERIC, test for COMP-3 fields
- F.2 Changes Affecting Version 3.1
- ISOLATE-FILE-CREATES
- ISOLATE-FILE-CREATES
- item help
- 10.2 Help Modes
J
- justification of data, using C$JUSTIFY
- C$JUSTIFY Routine
- JUSTIFIED clause, general format
- 5.7.1.12 JUSTIFIED clause
- JUSTIFIED, with formatted and centering option
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- JUSTIFY-NUM-FIELDS
- JUSTIFY-NUM-FIELDS
K
- KEY AREA
- MERGE Statement
- key fields
- 5.3 XFD Files
- key fields (by either explicit or implicit redefinition)
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- key interpretation
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- KEY IS phrase
- 5.3 XFD Files
- key letters, specifying for a menu
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- key mapping
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- key translation
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- KEYBOARD
- KEYBOARD
- keyboard additions under Windows NT
- M.3.2 Keyboard Differences
- keyboard configuration, default
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- keyboard configuration, saving
- C$KEYMAP Routine
- keyboard differences, Windows and DOS
- M.2.2 Keyboard Differences
- keyboard functions, and Terminal Manager
- 4.3 The Keyboard Interface
- keyboard input buffer, adding characters to
- W$KEYBUF Routine
- keyboard interface
- 4.3 The Keyboard Interface
- KEYBOARD variable
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- keyboard, redefining
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- KEY-MAP
- KEY-MAP
- keymap, specifying for alfred
- 3.5.4 Starting alfred
- Keys, example code
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- keys, list of function codes to represent
- 4.6 The Terminal Database File
- keys, performance considerations
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- keys, sample code
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- keys, split
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- keys, table of actions
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- KEYSTROKE
- KEYSTROKE
- keystroke, library routine to retrieve next
- W$GETC Routine
- key-table, requirements in MERGE statement
- MERGE Statement
- key-table, requirements in SORT statement
- SORT Statement
- KEY-TYPE field, list of codes
- SORT Statement
- kill -9
- 6.1 Handling Files
- 6.7 Exiting from ACUCOBOL-GT Programs
L
- LABEL control
- 5.3 Label
- LABEL RECORDS
- 5.4.6 LABEL RECORDS Clause
- LANs, installation on
- A.3.2 Network Environments
- large data handling
- 5.1.6 Large Data Handling
- large-model programs
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- LAST THREAD
- WAIT Statement
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- LEFT-TEXT, CHECK-BOX style
- 5.6 Check-Box
- LEFT-TEXT, RADIO-BUTTON special property
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- LESS THAN condition
- 6.3.1 Relation Conditions
- level 88
- 5.2.4 Condition-Name (Level 88)
- 5.7.1.14 VALUE clause
- level-number 01
- 5.1.2 Level-Numbers
- level-number 66
- 5.1.2 Level-Numbers
- level-number 77
- 5.1.2 Level-Numbers
- level-number 78
- 5.1.2 Level-Numbers
- level-number 88
- 5.1.2 Level-Numbers
- level-numbers
- 5.1.2 Level-Numbers
- level-numbers, syntax and general rules
- 5.7.1.1 Level-number
- LIB$GET_SYMBOL Routine
- LIB$GET_SYMBOL Routine
- LIB$SET_SYMBOL Routine
- LIB$SET_SYMBOL Routine
- library routines
- ACUCOBOL-GT Library Routines
- license file
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- license files
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- license management file
- 5.2.1 System Requirements
- License Management on DOS and Windows Systems
- 2.11.1 License Management on DOS and Windows Systems
- licenses, multiple-user
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- limitations, vio
- 3.4.4 Known Limitations
- limits and ranges of the compiler
- B.1 Limits and Ranges
- limits on open files
- 6.1.9 Limits on Open Files
- LINAGE
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- WRITE Statement
- LINAGE CLAUSE, and WRITE statement
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- LINAGE, general format
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- LINAGE-COUNTER
- 5.2.1 Qualification
- WRITE Statement
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- LINE Clause
- 5.9.4 LINE Clause
- line drawing
- 4.6.6 Line Drawing
- line drawing, and terminal manager
- 6.2.2 Terminal Manager Restrictions
- LINE NUMBER, DISPLAY SUBWINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- line segments requiring multiple-character escape sequences
- 4.6.6 Line Drawing
- line sequential file, creating an indexed file from
- 3.3.8 Loading a File
- line sequential files, ACUCOBOL-GT rules
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- line sequential files, uploading from Vision files to
- 3.3.7 Unloading to Binary and Line Sequential Format
- line wrapping
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- LINE, DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- LINE, line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- lines, creating graphical, see BAR control
- 5.11 Bar
- LINES, DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- LINES, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- lines, with 3-dimensional shading
- 9.9.2 Drawing 3-D Lines
- LINK TO THREAD
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- Linkage Section
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- 5.3 Data Division Format
- CALL Statement
- Linkage Section, general format
- 5.6 LINKAGE Section
- linking the runtime
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- linking the runtime, procedure
- C.5 Creating a New Runtime System
- LIST BOX:data truncated
- F.2 Changes Affecting Version 3.1
- list box:updating with the MODIFY verb
- MODIFY Statement
- LIST-BOX control
- 5.8 List-Box
- LIST-BOX control: PAGED, described
- 3.9 Paged List Boxes
- LIST-BOX control: PAGED: adding records to
- 3.9.2 Adding Records to a Paged List Box
- LIST-BOX control: PAGED: code example
- 3.9.5 Paged List Box Example
- LIST-BOX control: PAGED: event handling
- 3.9.4 Paged List Box Event Handling
- LIST-BOX:common properties
- 5.8 List-Box
- LIST-BOX:data limit
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- LIST-BOX:last item inserted twice
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- LIST-BOX:size limit
- 5.8 List-Box
- LIST-BOX:styles
- 5.8 List-Box
- Listing Options
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- listing options, compiler options
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- LISTS-UNBOXED
- LISTS-UNBOXED
- literals
- 2.1.2 Literals
- Loading a File
- 3.3.8 Loading a File
- local printers, assigning files to
- 2.8.3 Assigning Files to Local Printers
- local printing
- C$LOCALPRINT Routine
- LOCALPRINT
- 2.8.3 Assigning Files to Local Printers
- LOCK
- LOCK
- LOCK Statement
- LOCK Statement
- LOCK THREAD
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- LOCK THREAD statement, general format
- LOCK Statement
- LOCK THREAD, general rules
- LOCK Statement
- LOCK-DIR
- LOCK-DIR
- 6.1.5 Device Locking Under UNIX
- LOCKED-RECORD-DELAY
- LOCKED-RECORD-DELAY
- LOCK-HOLDING
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- locking method for Vision files
- V-LOCK-METHOD
- locking rules for transaction management
- 5.1.4 Extended Locking Rules
- locking threads
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- LOCKING-RETRIES
- LOCKING-RETRIES
- LOCK-OUTPUT
- LOCK-OUTPUT
- LOCK-SORT
- LOCK-SORT
- LOCKS-PER-FILE
- LOCKS-PER-FILE
- log files, multiple
- 5.1.6 Multiple Log Files
- LOG-BUFFER-SIZE
- LOG-BUFFER-SIZE
- LOG-DEVICE
- LOG-DEVICE
- LOG-DIR
- LOG-DIR
- LOG-ENCRYPTION
- LOG-ENCRYPTION
- LOG-FILE
- LOG-FILE
- LOGGING
- LOGGING
- logging and rollback of file update operations
- 5.1.5 Logging and Rollback of File Update Operations
- logging, configuration variables used with
- 5.1.7 Configuration Variables
- logging, specifying log files for
- 5.1.6 Multiple Log Files
- logical operators
- 6.3.6 Complex Conditions
- logical page
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- logical page, evaluation of
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- logutil
- 3.6 logutil
- logutil log file editor
- 3.6 logutil
- logutil options
- 3.6.2 Options
- logutil report headings
- 3.6.3 logutil Report Headings
- logutil syntax
- 3.6.1 Syntax
- lost records
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- lower-case words
- Lower-case Words
- lower-case words in manual
- 1.1.2 Lower-Case Words
- lowercase, converting
- C$TOUPPER and C$TOLOWER Routines
- LOWERED, FRAME style
- 5.10 Frame
- low-level debugging
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- LOW-VALUES
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
M
- M$ALLOC (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$ALLOC (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$FREE (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$FREE (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$GET (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$GET (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$PUT (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- M$PUT (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- Macro Debugger
- 3.1.5 Macro Debugger
- macros, in debugger
- 3.1.5 Macro Debugger
- magic cookie terminals
- RESTRICTED-VIDEO-MODE
- magic cookie, and attribute settings
- 4.6.3 Video Attributes
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- main application window:creating for optimal CELL size
- 1.6.3 Tips for Solving Cross Platform Interface Problems
- main application window:defined
- 1.4 Windowing Concepts
- main application window:DESTROY has no effect
- DESTROY Statement
- makefile
- C.5 Creating a New Runtime System
- MAKE-ZERO
- MAKE-ZERO
- mapping options
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- MASS-UPDATE
- MASS-UPDATE
- OPEN Statement
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- MASS-UPDATE, described
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- MASS-UPDATE, OPEN with
- OPEN Statement
- MASS-UPDATE, when to use
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- matching C Data Items
- C.4 Matching C Data Items
- MAX-ERROR-LINES
- MAX-ERROR-LINES
- MAX-FILES
- MAX-FILES
- max-lines
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- MAX-LOCKS
- MAX-LOCKS
- max-size
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- MAX-VAL
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- memory access violations
- 6.4.1 Memory Access Violations
- memory available on Windows NT
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- memory management
- C$CHAIN Routine
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- 6.3 Memory Management
- SORT-MEMORY
- memory management, initial programs
- 3.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
- memory, copying with C$MEMCPY
- C$MEMCPY (Dynamic Memory Routine)
- memory, more through C$CHAIN
- C$CHAIN Routine
- memory, routines to manage
- Routines to Handle Dynamic Memory
- memory, shared
- 2.12 acushare Utility Program
- SHARED-CODE
- memory, System-Space
- SYSTEM-SPACE
- menu activation keys, not configurable under Windows
- 11.1.4 Regarding Configuration Variables
- menu bar, static
- 8.1.1 Static Menu Bars
- menu bars
- 8.0 Creating Menu Bars and Pop-Up Menus
- menu bars, pop-up
- 8.1.2 Pop-Up Menu Bars
- menu blocking-count
- W$MENU Routine
- menu configuration with the generic menu handler
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- menu creation shortcut
- 8.4 Creating Menus-the Shortcut
- menu entries, properties
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- menu events
- 6.3 Menu Events
- menu facilities, graphical
- 8.2 Graphical Menu Facilities
- menu handling, overview
- 8.3 Overview of Menu Handling
- menu input
- 8.6 Menu Input
- menu item, disabling at creation time
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- menu item, placing a check mark beside
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- menu items, disabling dynamically
- 8.8.1 Disabling Menu Items
- menu operations, common
- 8.8 Common Menu Operations
- menu selection limits
- 8.6.2 Menu Selection Limits
- menu separators
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- menu shortcut keys
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- menu, adding item with W$MENU
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- menu, changing an item
- W$MENU Routine
- menu, deleting an item
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- menu, disabling an item at creation
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- menu, disabling entire
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.8.3 Disabling an Entire Menu
- menu, displayed in floating windows
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- menu, example using W$MENU
- 8.12 Menu Handling-Sample Code
- menu, saving the current one
- W$MENU Routine
- menubar, caution about sample programs
- 8.15 menubar Considerations
- MENU-ITEM
- MENU-ITEM
- MENU-ITEM configuration variable
- 8.7 Changing Menu Results
- menus and floating windows
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- menus, activation and use
- 8.5 Menu Activation and Use
- menus, adding and removing check marks
- 8.8.2 Checking Menu Items
- menus, and ACCEPT statement
- 8.6 Menu Input
- menus, and exception keys
- 8.6 Menu Input
- menus, and portability concerns
- 8.14 Portability Concerns
- menus, changing default action of an item
- 8.7 Changing Menu Results
- menus, check mark character
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- menus, color attributes
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- menus, configuration with generic menu handler
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- menus, controlling with W$MENU
- W$MENU Routine
- menus, defining menu keys
- 8.5.1 Defining Menu Keys
- menus, generic menu handler
- 8.2 Generic Menu Handler
- menus, pop-up
- 8.0 Creating Menu Bars and Pop-Up Menus
- menus, static and pop-up
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- menus, submenu character
- 8.11 Menu Configuration with the Generic Menu Handler
- menus, using them
- 8.6 Menu Input
- menus:incompatible with BOXED style
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- MERGE
- MERGE
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE, ASCENDING phrase
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE, general rules
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE, list of KEY-TYPE codes
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE, merge keys
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE, OUTPUT PROCEDURE
- MERGE Statement
- MERGE, variable-size table
- MERGE Statement
- message box
- 1.8 Sample Programs
- message boxes
- DISPLAY MESSAGE BOX
- message boxes in Windows
- M.2.1 Message Boxes
- message boxes under Windows NT
- M.3.1 Message Boxes
- message events for controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- message processing during file I/O
- F.2 Changes Affecting Version 3.1
- message queue, controlling the size of
- MESSAGE-QUEUE-SIZE
- MESSAGE-BOX-COLOR
- MESSAGE-BOX-COLOR
- MESSAGE-QUEUE-SIZE
- MESSAGE-QUEUE-SIZE
- messages, broadcasting
- SEND Statement
- messages, receiving
- RECEIVE Statement
- messages, sending
- SEND Statement
- messaging among threads
- 6.8.3 Thread Communication
- Micro Focus files, converting with vutil
- 3.3.12 Converting Micro Focus Files
- Microsoft Windows operating systems
- 1.3 Microsoft Windows Operating Systems
- min-lines
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- MIN-REC-SIZE
- MIN-REC-SIZE
- min-size
- DISPLAY INITIAL WINDOW
- MIN-VAL
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- Miscellaneous Commands
- 3.3.13 Miscellaneous Commands
- mnemonic-name, defined
- ACCEPT Statement
- modal window
- 2.1 Overview
- modeless window
- 2.1 Overview
- modeless windows, managing with threads
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- 6.8 Multiple Execution Threads
- modes, standard and auto
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
- MODIFY
- MODIFY
- MODIFY Statement
- MODIFY Statement
- monitor
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- MONOCHROME
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- MONOCHROME
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- monochrome monitor
- 9.1 Overview of Color Choices
- MOUSE
- MOUSE
- mouse actions, how handled
- 7.3 How Mouse Actions Are Handled
- mouse buttons
- 7.1 Mouse Properties
- mouse clicking
- 7.1 Mouse Properties
- mouse event, not returned to program
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- mouse exception values
- 7.3.1 Mouse Exception Processing
- mouse handling, automatic
- 7.4 Automatic Mouse Handling
- mouse handling, sample code
- 7.7 Mouse Handling-Sample Code
- mouse outside application window
- 7.2 Mouse Action Ownership in Graphical Environments
- mouse properties
- 7.1 Mouse Properties
- mouse shape
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- mouse, assigning values to actions
- 7.3.2 Assigning Results to Mouse Actions
- MOUSE, configuration variable
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- mouse, controlling with W$MOUSE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- mouse, excluding fields from selection by
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- mouse, in character-based environments
- 7.1 Mouse Properties
- mouse, in graphical environments
- 7.2 Mouse Action Ownership in Graphical Environments
- mouse, interaction with controls
- 3.7 Controls and the Mouse
- mouse, key code table
- 7.3.1 Mouse Exception Processing
- mouse, library routine for controlling
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- mouse, owned by which window
- 7.2 Mouse Action Ownership in Graphical Environments
- MOUSE, UNMASKING THE
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- mouse, using to position cursor
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- mouse, using with debugger
- 3.1.2 Cursor and Mouse Handling in Source-Level Debugging
- mouse:managing
- 3.7 Controls and the Mouse
- MOUSE-FLAGS
- 3.7 Controls and the Mouse
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- 7.3.3 Unmasking Mouse Actions
- MOUSE-FLAGS
- MOUSE-FLAGS doesn't work
- 11.1.4 Regarding Configuration Variables
- Mouse Support for X Terminals
- 4.6.8 Mouse Support for X Terminals
- MOVE
- MOVE
- MOVE, converting data type
- MOVE Statement
- MOVE, CORRESPONDING option
- 6.4.5 CORRESPONDING Option
- MOVE, general format
- MOVE Statement
- MOVE, illegal moves
- MOVE Statement
- MOVE, table of allowed sources and destinations
- MOVE Statement
- MPE/iX printing issues
- A.8.2 Printing from the MPE/iX Shell
- MPE/iX, installation
- A.8 HP3000 Machines Running MPE/iX
- MS-DOS Considerations
- 3.4.2 MS-DOS Considerations
- MS-DOS, and COMMIT statement
- COMMIT Statement
- MS-DOS, filenames
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- MS-DOS, installation
- A.3 MS-DOS and OS/2 Machines
- MS-DOS, line sequential files
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- MSG events for controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG events for windows
- 6.1 Window Events
- MSG-CLOSE
- 6.1 Window Events
- MSG-END-MENU
- 8.9 Pop-Up Menus
- MSG-GRID-RBUTTON-DOWN
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-GRID-RBUTTON-UP
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-INIT-MENU
- 8.9 Pop-Up Menus
- MSG-MENU-INPUT
- 8.9 Pop-Up Menus
- MSG-PAGED-FIRST
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-PAGED-LAST
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-PAGED-NEXT
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-PAGED-NEXTPAGE
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-PAGED-PREV
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-PAGED-PREVPAGE
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-SPIN-DOWN
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-SPIN-UP
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-TV-DBLCLICK
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-TV-EXPANDED
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-TV-EXPANDING
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-TV-SELCHANGE
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-TV-SELCHANGING
- 6.2 Control Events
- MSG-VALIDATE
- 6.6 Data Validation
- MULTILINE, TAB style
- 5.13 Tab
- multiple execution threads
- 6.8 Multiple Execution Threads
- multiple log files
- 5.1.6 Multiple Log Files
- multiple receiving fields
- 6.4.2 Multiple Receiving Fields
- multiple record definitions and XFDs
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- Multiple-User License Management
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- multiplication
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- MULTIPLY
- 6.4.1 Arithmetic Operations
- MULTIPLY
- MULTIPLY, general format
- MULTIPLY Statement
- multithreading and multiprocessor Systems
- 6.8.7 Multithreading and Multiprocessor Systems
- multithreading, see threads
- 6.8 Multiple Execution Threads
N
- name aliasing for files
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- NAME directive
- 5.3.3.6 Name Directive
- NAME_EXT_DATA_FMT
- NAME_EXT_DATA_FMT
- NAME_EXT_INDEX_FMT
- NAME_EXT_INDEX_FMT
- name-VERSION
- name-VERSION
- Naming the XFD
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- negated condition, language skeleton
- Negated Condition
- networks
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- networks, installation
- A.3.2 Network Environments
- NeXT, and function keys
- A.5.3.3 Function keys on the NeXT
- NeXT, and program execution
- A.5.3.2 Running ACUCOBOL-GT programs on the NeXT
- NeXT, and record locking
- A.5.3.1 Before you run ACUCOBOL-GT programs on the NeXT
- NeXT, installation procedures
- A.5.3 Installing on NeXT Machines Running UNIX
- NO SCROLL
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- NO WRAP
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- NO-BOX, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- NO-CONSOLE
- NO-CONSOLE
- nonnumeric literals
- 2.1.2.2 Nonnumeric literals
- nonnumeric operands, comparison of
- 6.3.1.2 Comparison of nonnumeric operands
- NO-SEARCH, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- NOT
- 6.3.3 Sign Condition
- 6.3.6 Complex Conditions
- NOT operation
- CBL_NOT Routine
- NO-TAB, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- Notation
- 1.6 Notation
- notation, of commands
- 1.6 Notation
- notation, used in Reference Manual
- 1.1 Conventions Used in this Manual
- notify events for controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- NOTIFY, CHECK-BOX style
- 5.6 Check-Box
- NOTIFY-DBLCLICK, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- NOTIFY-SELCHANGE, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- NTF events for controls
- 6.2 Control Events
- NULL, in PROCEDURE phrase
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- NULLS
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- numeric
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- NUMERIC condition
- 6.3.2 Class Condition
- NUMERIC directive
- 5.3.3.7 Numeric Directive
- numeric edited
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- numeric literals
- 2.1.2.1 Numeric literals
- numeric operands, comparison of
- 6.3.1.1 Comparison of numeric operands
- numeric value, conversion to
- MOVE Statement
- NUMERIC-VALIDATION
- NUMERIC-VALIDATION
- NUM-COL-HEADINGS, GRID special property
- 5.15 Grid
O
- Object Computer Entry
- Object Computer Entry
- object file
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- object file utilities
- 3.2 Object File Utilities-cblutil
- Object File Utilities-cblutil
- 3.2 Object File Utilities-cblutil
- object files, command to get information
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- Object Libraries
- 3.2.1 Object Libraries
- object libraries, creating
- 3.2.2 Creating Object Libraries
- object libraries, options when creating
- 3.2.2 Creating Object Libraries
- object library
- 3.2.1 Object Libraries
- object module, three states
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- object-code file
- 2.1 Using the Compiler
- OBJECT-COMPUTER paragraph
- 4.1.2 Object-Computer Paragraph
- OCCURS
- 5.1.5 Table Handling
- OCCURS clause in Screen Section
- 5.9.3 OCCURS Clause
- OCCURS clause and XFDs
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- OCCURS clause, general format
- 5.7.1.10 OCCURS clause
- OCCURS clause, general rules
- 5.7.1.10 OCCURS clause
- OCCURS clause, syntax rules
- 5.7.1.10 OCCURS clause
- OCCURS, table example
- 5.1.5 Table Handling
- Octal to ASCII Conversion
- OCTAL2ASCII Routine
- OLE Automation Server
- M.3.6 Calling ACUCOBOL-GT From Other Programming Languages
- OMITTED option
- DISPLAY src-item
- ON EXCEPTION
- MOVE Statement
- OPEN
- OPEN
- Open dialog box
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- Open dialog box:error handling
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- Open dialog box:memory management
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- open files, limits on and control of
- 6.1.9 Limits on Open Files
- OPEN, general format
- OPEN Statement
- OPEN, MASS-UPDATE option
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- opensave.def
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- OPENSAVE-DATA group item
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- OPENSAVE-DATA group item:memory management
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- operating system command, executing
- SYSTEM Routine
- operating system command, executing from Windows
- C$RUN Routine
- operating systems supported
- 1.4 Supported Hardware
- operations, AND
- CBL_AND Routine
- operations, EQUALS
- CBL_EQ Routine
- operations, exclusive OR
- CBL_XOR Routine
- operations, NOT
- CBL_NOT Routine
- operations, OR
- CBL_OR Routine
- operators
- 6.2.1 Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions
- 6.3.6 Complex Conditions
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- operators, list of relational
- 6.3.1 Relation Conditions
- OPTIONAL
- OPEN Statement
- options, runtime
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- OR
- 6.3.6 Complex Conditions
- OR operation
- CBL_OR Routine
- order of evaluation
- 6.2.1 Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions
- order of evaluation, condition
- 6.3.7 Order of Evaluation
- organization, of a COBOL program
- 2.5 Program Organization
- OS/2, installation
- A.3 MS-DOS and OS/2 Machines
- OTHER
- 5.3.3.11 When Directive
- OUTPUT PROCEDURE
- SORT Statement
- overflow condition, UNSTRING
- UNSTRING Statement
- OVERLAP-LEFT, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- OVERLAP-LEFT, style
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- OVERLAP-TOP, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- overlays
- 4.1.2 Object-Computer Paragraph
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- overlays in source, compiler option
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
P
- padding characters
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- page length of listings
- 2.1.2 Listing Options
- paged list box, creating
- 3.9.1 Creating a Paged List Box
- PAGED list box: adding records to
- 3.9.2 Adding Records to a Paged List Box
- PAGED list box: code example
- 3.9.5 Paged List Box Example
- PAGED list box: described
- 3.9 Paged List Boxes
- PAGED list box: event handling
- 3.9.4 Paged List Box Event Handling
- PAGED, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- PAGE-EJECT-ON-CLOSE
- PAGE-EJECT-ON-CLOSE
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- paint tool, creating bitmaps with
- 3.8.1 Drawing the Image
- paragraph header
- 2.5.1.3 Paragraph header
- parameter
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- parameters, finding size of passed
- C$PARAMSIZE Routine
- parameters, number passed to current program
- C$NARG Routine
- parameters, passing to called programs
- CALL Statement
- parent window
- 2.4 Parent and Child Windows
- parentheses, order of evaluation
- 6.3.7 Order of Evaluation
- 6.2.1 Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions
- pausing program, with C$SLEEP
- C$SLEEP Routine
- PC/TCP Kernel Software
- 5.2.1 System Requirements
- PERFORM
- PERFORM
- perform stack
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- PERFORM THREAD
- PERFORM Statement
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- PERFORM, general format
- PERFORM Statement
- PERFORM, general rules
- PERFORM Statement
- PERFORM, rules for transfer of control
- PERFORM Statement
- PERFORM, TEST AFTER
- PERFORM Statement
- PERFORM, TEST BEFORE
- PERFORM Statement
- performance under DEC OSF/1 AXP
- A.5.1.4 Performance under DEC OSF/1 AXP
- performance, improvement
- 6.3 Memory Management
- performance, improving
- 3.2.1 Object Libraries
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- 3.3.1 Examining File Information
- 6.2.1 Performance Considerations
- 6.1.6 Indexed File Considerations
- performance, improving with shared memory
- 2.12 acushare Utility Program
- SHARED-CODE
- PERFORM-STACK
- PERFORM-STACK
- PERMANENT, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- phone numbers, for technical support
- 1.7 How To Get Help
- PICTURE character string
- 2.1.3 Picture Strings
- PICTURE clause, and data classification
- 5.1.3 Classes of Data
- PICTURE clause, editing rules
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- PICTURE clause, general format
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- PICTURE clause, general rules
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- PICTURE string, repeat count example
- 5.7.1.1 Level-number
- PICTURE symbols and their functions
- 5.7.1.7 PICTURE clause
- PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- 5.9.1 PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- pipe
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- plug-in, how to display a message in the browser status bar
- W$STATUS Routine
- plug-in, passing a URL to a browser
- W$GETURL Routine
- pointer shape
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- POINTER, with STRING
- STRING Statement
- POP-UP AREA phrase
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- pop-up hints, with bitmap buttons
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- pop-up hints: configuration variables
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- pop-up menus
- 8.9 Pop-Up Menus
- 8.0 Creating Menu Bars and Pop-Up Menus
- pop-up window, scroll and wrap state
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- pop-up windows events for controls
- 6.3 Menu Events
- portability of XFDs
- 5.3 XFD Files
- portability, and menus
- 8.14 Portability Concerns
- portability, of bitmap buttons
- 3.8.5 Portability
- portability:user interface issues
- 1.6 Creating Portable User Interfaces
- portmap daemon
- 5.2.1 System Requirements
- positioning controls in a window
- 4.5 Coordinates
- POSITION-SHIFT, BAR
- 5.11 Bar
- print file
- WRITE Statement
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- print files
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- print functions, and Terminal Manager
- 4.6.10 Print Functions
- print records
- 5.1.7 File Types
- print spooler, Windows
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- print spooler:traditional, described
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- PRINT-CONTROL
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- PRINTER
- 2.8.2 File Name Examples
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- printer attached to terminal
- 4.6.10 Print Functions
- printers
- 2.8 File Name Interpretation
- printers, and ASSIGN clause
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- printers, assigning files to local
- 2.8.3 Assigning Files to Local Printers
- printers, local
- C$LOCALPRINT Routine
- printers, machine-independent access of
- 2.8.2 File Name Examples
- printing and spooler issues with Windows
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- printing from the MPE/iX shell
- A.8.2 Printing from the MPE/iX Shell
- printing problems, and device-dependent control sequences
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- printing under Windows
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- printing, and UNIX
- 6.1.5 Device Locking Under UNIX
- printing:support under Windows
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- PROCEDURE Clause
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- Procedure Division
- 6.1 Organization
- Procedure Division
- Procedure Division, flow of control
- 6.1.2 Flow of Control
- Procedure Division, organization
- 6.1 Organization
- Procedure Division, statements
- 6.6 Procedure Division Statements
- Procedure Division,syntax rules
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- processes allowed per runtime
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- Product Overview
- 1.1 Product Overview
- Program Execution Problems
- 1.7.2 Program Execution Problems
- program failure, and non-zero user count
- 3.3.1 Examining File Information
- program organization
- 2.5 Program Organization
- Program Organization
- program structure
- 2.0 Program Structure
- PROGRAM-ID
- 3.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
- PROMPTING
- PROMPTING
- protecting fields from mouse selection
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- p-step
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- PUSH BUTTON:status 96
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- PUSH-BUTTON control
- 5.5 Push-Button
- PUSH-BUTTON:bitmap button, introduced
- 3.8 Bitmap Buttons
- PUSH-BUTTON:common properties
- 5.5 Push-Button
- PUSH-BUTTON:styles
- 5.5 Push-Button
- PUSH-BUTTON:styles:NO-AUTO-DEFAULT
- 5.5 Push-Button
Q
- qualification
- 5.2.1 Qualification
- Qualification
- qualification, general format
- 5.2.1 Qualification
- qualification, language skeleton
- Qualification
- qualification, syntax rules
- 5.2.1 Qualification
- questions frequently asked
- 11.1 Frequently Asked Questions
- QUEUE-READERS
- QUEUE-READERS
- quit, handling Close under Windows
- 8.13 System Menu "Close" Handling under Windows
- QUIT-MODE
- QUIT-MODE
- QUIT-MODE configuration variable, to perform an orderly shutdown
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- QUIT-MODE, handling close under Windows
- 8.13 System Menu "Close" Handling under Windows
- QUOTES
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
R
- RADIO-BUTTON control
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- RADIO-BUTTON:bitmap button, introduced
- 3.8 Bitmap Buttons
- RADIO-BUTTON:common properties
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- RADIO-BUTTON:styles
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- RADIO-BUTTON:styles:BITMAP
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- RADIO-BUTTON:styles:FRAMED
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- RADIO-BUTTON:styles:UNFRAMED
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- RAISED, FRAME style
- 5.10 Frame
- READ
- READ
- READ NEXT, and locked records
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- READ PREVIOUS
- READ Statement
- READ, and record locking
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- READ, general format
- READ Statement
- READ, general rules
- READ Statement
- READ, rules for retrieving records
- READ Statement
- Rebuilding Files
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- RECEIVE
- RECEIVE
- 6.8.3 Thread Communication
- RECEIVE, general format
- RECEIVE Statement
- receiving fields, multiple
- 6.4.2 Multiple Receiving Fields
- RECORD clause
- 5.4.5 RECORD Clause
- record description entry
- 5.1.1 Record Description
- 5.7 Record Description Entry
- Record Description Entry
- record editor, alfred
- 3.5 Acucorp's Indexed File Record Editor-alfred
- record locking
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- record locking with transaction management
- 5.1.4 Extended Locking Rules
- record locking, performance considerations
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- record locking, UNLOCK
- UNLOCK Statement
- record locking, WITH NO LOCK
- READ Statement
- record size, BLOCK CONTAINS
- 5.4.4 BLOCK CONTAINS Clause
- records, adding, modifying, deleting from an indexed file
- 3.5 Acucorp's Indexed File Record Editor-alfred
- records, fixed-length
- 6.1 Handling Files
- records, four types
- 5.1.7 File Types
- records,variable-length
- 6.1 Handling Files
- recovery of files through transaction management
- 5.1.2 The Transaction Logging Process
- RECURSION
- RECURSION
- recursive PERFORM statements, potential problem
- F.2 Changes Affecting Version 3.1
- REDEFINES
- 5.7.1.3 REDEFINES clause
- REDEFINES clause and XFDs
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- redefining the keyboard
- 4.3.2 Redefining the Keyboard
- Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- Reference Manual
- 1.2.3 Reference Manual
- Reference Manual, summary of contents
- 1.2.3 Reference Manual
- reference modification
- 5.2.3 Reference Modification
- Reference Modification
- reference modification, code examples
- 5.2.3 Reference Modification
- reference modification, highlights for first-time users
- 5.2.3 Reference Modification
- reference modification, language skeleton
- Reference Modification
- REG__CLOSE_KEY, library routine
- REG_CLOSE_KEY Routine
- REG_CREATE_KEY, library routine
- REG_CREATE_KEY Routine
- REG_CREATE_KEY_EX, library routine
- REG_CREATE_KEY_EX Routine
- REG_DELETE_KEY, library routine
- REG_DELETE_KEY Routine
- REG_DELETE_VALUE, library routine
- REG_DELETE_VALUE Routine
- REG_ENUM_KEY, library routine
- REG_ENUM_KEY Routine
- REG_ENUM_VALUE, library routine
- REG_ENUM_VALUE Routine
- REG_OPEN_KEY, library routine
- REG_OPEN_KEY Routine
- REG_OPEN_KEY_EX, library routine
- REG_OPEN_KEY_EX Routine
- REG_QUERY_VALUE, library routine
- REG_QUERY_VALUE Routine
- REG_QUERY_VALUE_EX, library routine
- REG_QUERY_VALUE_EX Routine
- REG_SET_VALUE, library routine
- REG_SET_VALUE Routine
- REG_SET_VALUE_EX, library routine
- REG_SET_VALUE_EX Routine
- Related Documents
- 1.3 Related Documents
- relation conditions, abbreviated combined
- 6.3.8 Abbreviated Combined Relation Conditions
- relational conditions
- 6.3.1 Relation Conditions
- relational operators
- 6.3.1 Relation Conditions
- relative file, creating an indexed file from
- 3.3.8 Loading a File
- relative files
- 6.1.2 Relative Files
- relative files, organization of
- 5.1.7 File Types
- relative files, record length
- 6.1.2 Relative Files
- relative files, treatment on different machines
- 6.1.2 Relative Files
- REL-DELETED-VALUE
- REL-DELETED-VALUE
- RELEASE
- RELEASE
- RELEASE, general format
- RELEASE Statement
- RELEASE-MOUSE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- relinking the runtime
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- relinking the runtime, procedure
- C.5 Creating a New Runtime System
- remote file access with AcuServer
- 5.2 AcuServer
- remote name notation with C$COPY
- C$COPY Routine
- remote name notation with SORT-DIR
- SORT-DIR
- remote name notation with XFD-DIRECTORY
- XFD-DIRECTORY
- remote name notation, definition
- 5.2.2 Remote Name Notation
- remote name notation, naming the object code file
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- remote name notation, specifying file aliases
- 2.7.1 File Name Assignments
- RENAME Routine
- RENAME Routine
- RENAME, library routine
- RENAME Routine
- RENAMES clause, general format
- 5.7.1.15 RENAMES clause
- RENEW-TIMEOUT
- RENEW-TIMEOUT
- REPLACE statement, code examples
- 2.4.2 The REPLACE Statement
- REPLACE, general rules
- 2.4.2 The REPLACE Statement
- REPLACE, syntax rules
- 2.4.2 The REPLACE Statement
- REPLACE, text replacement rules
- 2.4.2 The REPLACE Statement
- REPLACING, INSPECT with
- INSPECT Statement
- REQUIRED
- 6.6 Data Validation
- required functions, terminal manager
- 4.6.1 Required Functions
- Reserved Word Options
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- reserved words, compiler options for listing
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- reserved words, compiler options for suppression of
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- reserved words, complete list
- D.1 Introduction
- Resetting User Counts
- 3.3.4 Resetting User Counts
- RESIDENT
- 3.1 PROGRAM-ID Paragraph
- RESIZE-FRAMES
- RESIZE-FRAMES
- RESIZE-FREELY
- RESIZE-FREELY
- resource files:adding to an object library with cblutil
- 3.2.2 Creating Object Libraries
- resource files:as used by W$BITMAP
- W$BITMAP Routine
- resource files:defined
- 2.5.1 Resource Files
- resource files:how to include in object files
- 2.4.1 The COPY Statement
- resource files:loading with W$BITMAP
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- resource files:rules for
- 2.5.1 Resource Files
- restricted attribute handling
- 4.5 Restricted Attribute Handling
- restricted video modes
- 4.5.1 Restricted Video Modes
- RESTRICTED-VIDEO-MODE
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- RESTRICTED-VIDEO-MODE
- RESTRICTED-VIDEO-MODE, and special terminals
- 4.5.1 Restricted Video Modes
- restrictions on compiler
- B.3 Restrictions
- results, unpredictable if sending and receiving item share storage area
- 6.4.6 Unpredictable Results
- RETURN
- RETURN
- RETURN, general format
- RETURN Statement
- RETURN-CODE
- EXIT Statement
- RETURN-CODE, EXIT
- EXIT Statement
- RETURN-CODE, from SYSTEM
- SYSTEM Routine
- RETURN-CODE, GOBACK
- GOBACK Statement
- RETURN-CODE, STOP
- STOP Statement
- RETURN-UNSIGNED
- EXIT Statement
- GOBACK Statement
- REVERSE, in line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- REVERSE, with DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- REVERSED, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- REWRITE
- REWRITE
- REWRITE, and record locking
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- REWRITE, general format
- REWRITE Statement
- RM/COBOL, reserved words option
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- RM/COBOL
- 5.7.1.11 SYNCHRONIZED clause
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
- RM/COBOL compatibility, compiler option
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- RM/COBOL version 2 (ANSI 74), file status codes
- J.1 Introduction
- RM/COBOL version 2, converting programs
- 6.3 Memory Management
- RM/COBOL, and file status codes
- 2.7.3 File Status Codes
- RM/COBOL, AUTO phrase
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- RM/COBOL, compatibility mode
- 2.3 Compiler Compatibility Modes
- RM/COBOL, compatibility mode, and locked records
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- RM/COBOL, compile-time options
- E.1 Compile-Time Options
- RM/COBOL, conversion guide
- E.1 Compile-Time Options
- RM/COBOL, conversion of RM/COBOL-85 data files
- 6.1.7 Converting RM/COBOL Data Files
- RM/COBOL, conversion of Version 2 data files
- 6.1.7 Converting RM/COBOL Data Files
- RM/COBOL, ERASE
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY src-item
- RM/COBOL, memory management
- E.3 Memory Management
- RM/COBOL, min-blocks
- 5.4.4 BLOCK CONTAINS Clause
- RM/COBOL, reserved words
- D.1 Introduction
- RM/COBOL, runtime options
- E.2 Runtime Options
- RM/COBOL, treatment of spooled print files
- 6.3 Memory Management
- RM/COBOL, USE AFTER EXCEPTION
- READ Statement
- RM/COBOL, version 2, file handling
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- RM/COBOL-85
- E.1 Compile-Time Options
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- RM/COBOL-85 (ANSI 85), file status codes
- J.1 Introduction
- RM/COBOL-85 indexed files, converting with vutil
- 3.3.10 Converting RM/COBOL-85 Indexed Files
- rollback
- 5.1.2 The Transaction Logging Process
- ROLLBACK
- ROLLBACK in FILE-CONTROL, effect on COMMIT
- COMMIT Statement
- ROLLBACK statement, general format
- ROLLBACK Statement
- rollback, automatic
- ROLLBACK Statement
- ROLLBACK, implicit
- 5.1.3 Transaction Management Verbs
- ROUNDED phrase
- 6.4.3 ROUNDED Option
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- Routines to Handle Dynamic Memory
- Routines to Handle Dynamic Memory
- run all threads
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- Run option under Windows
- A.4.4 Running your programs
- run unit
- CALL Statement
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- CHAIN Statement
- run units, and open files
- OPEN Statement
- running programs simultaneously
- C$RUN Routine
- running programs under Windows
- A.4.4 Running your programs
- Runtime Configuration
- 2.7 Runtime Configuration
- runtime configuration file
- 4.1.1 Terminal Manager Functions
- runtime configuration file names
- 4.2.3 Step three- Configuration Variables
- runtime configuration variables
- 2.7 Runtime Configuration
- runtime debugger
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- runtime execution for Windows
- A.4.4 Running your programs
- runtime messages, controlling text of
- TEXT
- runtime option, assembly language flag
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- runtime system
- 2.1 Using the Compiler
- runtime, calling from other programming languages
- M.3.6 Calling ACUCOBOL-GT From Other Programming Languages
- runtime, creating a new under Windows NT
- M.3.5 Using the SDK
- runtime, introduction
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- runtime, options
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- runtime, parameters
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- runtime, size
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- runtime, installation
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- runtime: creating new under Windows
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- runtime: relinking
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- runtime: removing optional components
- 2.10 Reducing the Size of the Runtime
- Ryan McFarland COBOL
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
S
- safe mode exit
- 6.7 Exiting from ACUCOBOL-GT Programs
- SAME AREA
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- SAME RECORD AREA
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- SAME SORT AREA
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- sample programs
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- sample programs for user interfaces
- 1.8 Sample Programs
- Save As dialog box
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- Save As dialog box:error handling
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- Save As dialog box:memory management
- C$OPENSAVEBOX Routine
- save the current menu
- W$MENU Routine
- save-area
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- scope of statements
- 6.1.1.1 Scope of statements
- scope-delimited statement
- 6.1.1.1 Scope of statements
- SCREEN
- SCREEN
- Screen Description Entry
- Screen Description Entry
- screen description entry, general format
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- Screen Description, and FROM
- 5.9.1 PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- screen description, and OCCURS
- 5.9.3 OCCURS Clause
- Screen Description, and PICTURE
- 5.9.1 PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- Screen Description, and TO
- 5.9.1 PICTURE, FROM, TO, and USING Clauses
- screen description, and VALUE
- 5.9.2 VALUE Clause
- screen description, general rules
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- screen description, syntax rules
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- screen functions, additional
- 4.6.2 Additional Screen Functions
- screen import, case of text
- 2.1.6.1 Mapping options
- screen import, compiler option
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- screen importing
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- SCREEN Option
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- screen scrolling,
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- Screen Section
- 6.4.9 Common Screen Options
- Screen Section , general format
- 5.8 Screen Section
- Screen Section entries, defined
- 5.8 Screen Section
- Screen Section, advantages
- 6.5.4 Comparison to Field-level
- 6.5.1 Advantages
- Screen Section, and CONVERT-OUTPUT
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- Screen Section, and mouse behavior
- 7.5 Screen Section Behavior
- Screen Section, COLUMN clause
- 5.9.5 COLUMN Clause
- Screen Section, comparison to field-level
- 6.5.4 Comparison to Field-level
- Screen Section, embedded procedures example
- 6.5.5 Using Screen Section Embedded Procedures
- Screen Section, example code
- 6.5.3 Syntax
- Screen Section, introduction to
- 6.5 Screen Section
- Screen Section, LINE clause
- 5.9.4 LINE Clause
- Screen Section, mouse handling in the
- 7.4 Automatic Mouse Handling
- Screen Section, OCCURS and COLOR examples
- 5.9.3 OCCURS Clause
- Screen Section, OCCURS-general rules
- 5.9.3 OCCURS Clause
- Screen Section, overview
- 5.8 Screen Section
- Screen Section, structure of
- 6.5.2 Structure
- Screen Section, syntax
- 6.5.3 Syntax
- Screen Section, three types of screen description entries
- 6.5.3 Syntax
- Screen Section,and ACCEPT/DISPLAY statements
- 6.5.3 Syntax
- Screen Section:AFTER procedure
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- Screen Section:CHARACTER label
- 5.9 Screen Description Entry
- 4.3 Graphical vs. Textual Modes
- Screen Section:event procedure
- 5.9.6 PROCEDURE Clause
- Screen Section:GRAPHICAL label
- 4.3 Graphical vs. Textual Modes
- SCREEN, configuration file entry
- SCREEN
- SCRIPT-STATUS
- SCRIPT-STATUS
- SCRIPT-STATUS, configuration file entry
- SCRIPT-STATUS
- SCROLL
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- SCROLL
- scroll and wrap states of the current window
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- scroll bar, debugger
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- SCROLL, configuration file entry
- SCROLL
- SCROLL-BAR control
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- SCROLL-BAR: common properties
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- SCROLL-BAR: special properties
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- SCROLL-BAR: styles
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- SCROLL-BAR:styles:HORIZONTAL
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- SCROLL-BAR:styles:TRACK-THUMB
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- scrolling
- SCROLL
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- SDK for Windows
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- SDK under Windows NT
- M.3.5 Using the SDK
- SDK, MS Software Development Kit
- 1.2.4 GUI Development with Third Party Kits and Tools
- SEARCH
- SEARCH
- search box, component of a paged list box
- 3.9.3 Other List Box Operations
- search path for copy libraries
- 2.5 Copy Libraries
- search paths, for code and data files
- 2.7.2 Code and Data File Search Paths
- SEARCH statement, code examples
- SEARCH Statement
- SEARCH statement, general format
- SEARCH Statement
- SEARCH statement, highlights for first-time users
- SEARCH Statement
- SEARCH, general rules
- SEARCH Statement
- SEARCH-OPTIONS, GRID special property
- 5.15 Grid
- SEARCH-TEXT, GRID special property
- 5.15 Grid
- secondary error codes for error 98s
- J.3 Vision Secondary Error Codes for Error 98s
- SECONDARY-TABLE directive
- 5.3.3.8 Secondary-Table Directive
- section header
- 2.5.1.2 Section header
- security
- A.1 License Files, Sample Programs and ".def" Files
- Security with alfred
- 3.5.2 Security
- segmentation
- 4.1.2 Object-Computer Paragraph
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- segmentation in source, compiler option
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- SEGMENT-LIMIT
- 4.1.2 Object-Computer Paragraph
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- SELECT verb
- 5.3 XFD Files
- SELECT statement
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- Selection item in debugger menu
- 3.1.2 Cursor and Mouse Handling in Source-Level Debugging
- SELECTION-TEXT, ENTRY-FIELD special property
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- SELF-ACT
- 4.2 Events
- SELF-ACT radio buttons act strange
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- SELF-ACT, CHECK-BOX style
- 5.6 Check-Box
- SELF-ACT, PUSH-BUTTON style
- 5.5 Push-Button
- SEND
- 6.8.3 Thread Communication
- SEND
- SEND Statement
- SEND Statement
- SEND, general format
- SEND Statement
- sentences, definitions
- 2.5.1.6 Sentences
- separators in menus
- 8.3.1 Properties of Menu Entries
- separators, rules
- 2.1.4 Separators
- sequence number
- 2.2.1 ANSI Format
- sequential files
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- sequential files, organization of
- 5.1.7 File Types
- serial numbers for runtimes
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- SERVER-NUMBER, configuration file entry
- SERVER-NUMBER
- SET
- SET
- SET ADDRESS OF Linkage data item
- SET Statement
- SET command
- 1.5 Environment Variables
- SET ENVIRONMENT
- H.1 Introduction
- SET Statement
- SET ENVIRONMENT, and color map
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- SET, general format
- SET Statement
- SET, general rules
- SET Statement
- SET:to set the priority value of a thread
- 6.8.4 Thread Priorities
- SET-DELAYED-MOUSE-SHAPE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- SET-MOUSE-HELP
- W$MOUSE Routine
- SET-MOUSE-POSITION
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- W$MOUSE Routine
- SET-MOUSE-SCREEN-POSITION
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- W$MOUSE Routine
- SET-MOUSE-SHAPE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- Shading
- Shading
- SHADING, BAR special property
- 5.11 Bar
- shading, use of
- 1.1.5 Shading
- SHADOW phrase
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- shadowed windows
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- SHARE, on DOS LANs
- A.3.2.1 Using SHARE with DOS
- shared memory
- 2.12.2 Using shared memory
- 2.12 acushare Utility Program
- SHARED-CODE, configuration file entry
- SHARED-CODE
- sharing code, on AOS/VS
- 2.12.2.2 Code sharing on AOS/VS
- sharing, indicating programs to share
- 2.12.2.1 Indicating programs to share
- shortcut keys, how to display on menus
- 8.4.1 Using genmenu
- SHUTDOWN-MESSAGE-BOX, configuration file entry
- SHUTDOWN-MESSAGE-BOX
- SIGN clause, general format
- 5.7.1.9 SIGN clause
- SIGN clause, general rules
- 5.7.1.9 SIGN clause
- sign condition
- 6.3.3 Sign Condition
- sign-storage conventions
- 2.1.7 Data Storage Options
- Simple Conditions
- #$K+Simple Conditions
- SIZE ERROR
- DIVIDE Statement
- SIZE ERROR clause
- 6.4.4 SIZE ERROR Option
- size error, effects on data values
- 6.4.4 SIZE ERROR Option
- SIZE, DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- SIZE, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- SIZE, in line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- skip to cursor line
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- software development for Windows Kit
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- SORT
- SORT
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- Sort File Description
- Sort File Description
- sort file description entry
- 5.4.2 Sort File Description Entry
- sort files, verbs used with of
- 5.1.7 File Types
- SORT general format
- SORT Statement
- sort key, KEY AREA option
- SORT Statement
- SORT, COLLATING SEQUENCE
- SORT Statement
- SORT, general rules
- SORT Statement
- SORT-DIR, configuration file entry
- SORT-DIR
- SORT-FILES, configuration file entry
- SORT-FILES
- SORT-MEMORY, configuration file entry
- SORT-MEMORY
- SORT-RESERVE, configuration file entry
- SORT-RESERVE
- sound, playing .WAV files and Windows' system sounds
- WIN$PLAYSOUND Routine
- Source Code Control
- 2.6 Source Code Control
- source code, excluding or including lines at compile time
- 2.6 Source Code Control
- source code, format of
- 2.4 Source Formats
- Source Computer Entry
- Source Computer Entry
- source debugging
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- source format
- 2.2 Source Format
- source format, as ANSI
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- Source Formats
- 2.4 Source Formats
- source management statements
- 2.4 Source Management Statements
- Source Options
- 2.1.5 Source Options
- source-code control and XFDs
- 5.3 XFD Files
- SOURCE-COMPUTER paragraph
- 4.1.1 Source-Computer Paragraph
- spaces, Strip-Trailing-Spaces
- STRIP-TRAILING-SPACES
- SPACES-ZERO, configuration file entry
- SPACES-ZERO
- special characters, in manual
- Upper-case and Special-Character Words
- Special Names Entry, language skeleton
- Special Names Entry
- special properties table
- 5.1.4 Special Properties Table
- special properties, context sensitive treatment
- 4.4 Styles and Special Properties
- SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- SPECIAL-NAMES switches
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- SPECIAL-NAMES, general format
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- SPECIAL-NAMES, in Data Division
- 5.7.1.5 IS SPECIAL-NAMES clause
- specifications, for ACUCOBOL-GT
- B.1 Limits and Ranges
- Specifying Addresses
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- SPINNER, ENTRY-FIELD style
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- split key
- 4.2.1 File-Control Paragraph
- Split keys
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- spooler and Windows
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- SPOOL-FILE, configuration file entry
- SPOOL-FILE
- SQUARE, CHECK-BOX style
- 5.6 Check-Box
- standard alignment rules
- 5.1.4 Standard Alignment Rules
- Standard Options
- 2.1.1 Standard Options
- standard, ANSI
- 1.2 Acknowledgment
- START
- START
- START TRANSACTION
- START Statement
- START TRANSACTION, implied
- START Statement
- START, and READ NEXT
- START Statement
- START, general format
- START Statement
- START, indexed files
- START Statement
- START, NOT INVALID KEY
- START Statement
- START, relative files
- START Statement
- START, warning about reverse file processing
- START Statement
- starting alfred
- 3.5.4 Starting alfred
- Starting and using acushare
- 2.12.3 Starting and using acushare
- statement rules, common
- 6.4 Common Statement Rules
- statements, conditional
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- statements, delimited-scope
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- statements, four types
- 2.5.1.5 Statements
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- statements, imperative
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- statements, termination of
- 6.1.1.1 Scope of statements
- statements,compiler-directing
- 6.1.1 Statements and Sentences
- statements,scope of
- 6.1.1.1 Scope of statements
- STATIC-LIST, COMBO-BOX style
- 5.9 Combo Box
- status 96
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- STATUS clause, switch-status name
- 6.3.5 Switch-Status Condition
- step
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- STOP
- STOP
- STOP RUN
- GOBACK Statement
- STOP Statement
- STOP Statement
- STOP Statement
- STOP THREAD
- STOP Statement
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- STOP, general format
- STOP Statement
- STOP-RUN-ROLLBACK, configuration file entry
- STOP-RUN-ROLLBACK
- STRING
- STRING
- STRING statement, highlights for first-time users
- STRING Statement
- STRING, general format
- STRING Statement
- STRING, NOT ON OVERFLOW phrase
- STRING Statement
- STRING, POINTER phrase
- STRING Statement
- STRING, with DELIMITED
- STRING Statement
- STRIP-TRAILING-SPACES
- STRIP-TRAILING-SPACES
- style numbers, defined in controls.def
- 5.1 The Components of a Control
- style properties table
- 5.1.3 Styles Table
- styles, context sensitive treatment
- 4.4 Styles and Special Properties
- styles, global
- 5.2 Global Styles
- SUB Interface for C routines
- C.3.1 The "SUB" Interface
- SUB85 interface for C routines
- C.3.2 The "SUB85" Interface
- submenus
- 8.1.3 Submenus
- 8.3 Overview of Menu Handling
- subprograms
- 3.2.1 Object Libraries
- 6.3 Memory Management
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- subprograms, calling
- 2.9 Calling Subprograms
- subprograms, caution about RM/COBOL and Zi option
- 6.3 Memory Management
- subscripting
- 5.2.2 Subscripting
- Subscripting
- subscripting, general format and syntax rules
- 5.2.2 Subscripting
- subscripting, language skeleton
- Subscripting
- SUBTRACT
- 6.4.1 Arithmetic Operations
- SUBTRACT
- SUBTRACT, CORRESPONDING option
- 6.4.5 CORRESPONDING Option
- SUBTRACT, general format
- SUBTRACT Statement
- SUBTRACT, general rules
- SUBTRACT Statement
- subtraction
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- subwindow
- 2.1 Overview
- subwindow:characteristics specified at runtime
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- subwindow:defined
- 1.5 ACUCOBOL-GT Window Types
- subwindow:video intensity
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- subwindows:compatibility with controls
- 3.3 Interaction between Controls and Windows
- subwindows:mixed with controls
- DISPLAY control-type-name
- support, what we need if you call us
- 1.7.2 Program Execution Problems
- supported hardware
- 1.4 Supported Hardware
- 1.4 Supported Hardware
- suspended thread
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- switches, example code
- 6.3.5 Switch-Status Condition
- switches, external program
- 6.3.5 Switch-Status Condition
- switches, in SPECIAL-NAMES
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- switches, SET statement
- SET Statement
- switches, SPECIAL-NAMES
- 2.2 Using the Runtime System
- SWITCH-PERIOD
- 6.8.4 Thread Priorities
- SWITCH-PERIOD
- SWITCH-PERIOD, configuration file entry
- SWITCH-PERIOD
- switch-status condition
- 6.3.5 Switch-Status Condition
- SYMBOLIC CHARACTERS
- 2.1.2.3 Figurative constants
- 4.1.3 Special-Names Paragraph
- symbolic debugging
- 3.1 Runtime Debugger
- 2.1.9 Miscellaneous Options
- SYNCHRONIZED, general format
- 5.7.1.11 SYNCHRONIZED clause
- syntax for XFDs
- 5.3.3 Syntax
- syntax, logutil
- 3.6.1 Syntax
- SYSTEM
- SYSTEM Routine
- system events, described
- 6.0 Events Reference
- System Menu
- 2.1 Overview
- system menu "Close" handling under Windows
- 8.13 System Menu "Close" Handling under Windows
- SYSTEM Routine
- SYSTEM Routine
- SYSTEM routine, using with Windows
- M.2.5 Differences between MS-DOS and Windows
- SYSTEM routine, using with Windows NT
- M.3.4 Special Characteristics of 32-bit Windows
- SYSTEM-SPACE, configuration file entry
- SYSTEM-SPACE
T
- TAB control
- 5.13 Tab
- table handling
- 5.1.5 Table Handling
- table of status codes
- J.2 Table of Codes
- table, example code
- 5.1.5 Table Handling
- tables, adding together
- ADD Statement
- TAB-TO-ADD, TAB special property
- 5.13 Tab
- TAB-TO-DELETE
- 5.13 Tab
- TALLYING, INSPECT with
- INSPECT Statement
- technical support
- 1.7 How To Get Help
- Televideo 925
- 4.5 Restricted Attribute Handling
- TEMP-DIR, configuration file entry
- TEMP-DIR
- temporary data item
- 6.4.1 Arithmetic Operations
- TEMPORARY, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- TEMPORARY-CONTROLS, configuration file entry
- TEMPORARY-CONTROLS
- TERM variable
- A.2.1 TERM Variable
- termcap
- 4.6 The Terminal Database File
- terminal charcateristics, by reference
- 4.6.11 Continued Entries
- terminal database
- A.2.2 Terminal Database
- terminal database file
- 4.2.1 Step one-Terminal Identification
- 4.1.1 Terminal Manager Functions
- terminal database file, by reference entry
- 4.6.11 Continued Entries
- terminal database file, editing
- 4.6 The Terminal Database File
- terminal database file, systems that don't use
- 4.2.1 Step one-Terminal Identification
- terminal definition
- 4.2.2 Step two-Terminal Definition
- terminal definition, DOS considerations
- 4.2.2 Step two-Terminal Definition
- Terminal format
- 2.4 Source Formats
- terminal function codes
- 4.1.1 Terminal Manager Functions
- 4.4 The Display Interface
- Terminal Handling Options
- 2.7.4 Terminal Handling Options
- terminal identification
- 4.2.1 Step one-Terminal Identification
- Terminal Manager Functions
- 4.1.1 Terminal Manager Functions
- Terminal Manager Restrictions
- 6.2.2 Terminal Manager Restrictions
- Terminal Manager, definition
- 4.1 How the Terminal Manager Works
- terminal manager, guidelines to improve performance
- 6.2.1 Performance Considerations
- Terminal Manager, installation
- A.2 Configuring Your Terminals
- Terminal Manager, introduction
- 4.1 How the Terminal Manager Works
- terminal manager, performance and screen I/O
- 6.2 Terminal I/O
- Terminal Manager, re-initializing
- W$FORGET Routine
- Terminal Manager, required functions
- 4.6.1 Required Functions
- terminal, source program format
- 2.2.2 Terminal Format
- terminals, getting ready
- 4.2 Getting Your Terminals Ready
- terminals, initialization strings
- 4.6.9 Initialization
- terminals, list of function codes for
- 4.6 The Terminal Database File
- terminals, non-ANSI conforming
- 4.5 Restricted Attribute Handling
- terminals, restrictions imposed by special
- 4.5.1 Restricted Video Modes
- terminating events, described
- 4.2 Events
- TERMINATION-VALUE
- 11.1.2 Regarding Controls
- Testing File Integrity
- 3.3.2 Testing File Integrity
- TEST-MOUSE-PRESENCE
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- W$MOUSE Routine
- Texas Instruments System 1500
- A.5.1.1 Texas Instruments System 1500
- Texas Instruments, installation
- A.5.1.1 Texas Instruments System 1500
- text records
- 5.1.7 File Types
- TEXT, configuration file entry
- TEXT
- TEXTSIZE-DATA
- W$TEXTSIZE Routine
- textual and graphical modes, mixed
- 4.3 Graphical vs. Textual Modes
- THAI, configuration file entry
- THAI
- thread communication
- 6.8.3 Thread Communication
- thread fundamentals
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- thread priorities
- 6.8.4 Thread Priorities
- threads and threading
- 6.8 Multiple Execution Threads
- threads, ANY THREAD
- WAIT Statement
- threads, controlling the switching period
- SWITCH-PERIOD
- DISPLAY-SWITCH-PERIOD
- threads, LAST THREAD
- WAIT Statement
- threads, starting
- CALL Statement
- threads, stopping
- STOP Statement
- threads, synchronizing
- WAIT Statement
- threads, to manage modeless windows
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- threads, unlocking
- UNLOCK Statement
- threads:broadcasting messages
- SEND Statement
- threads:creating
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- threads:effects on windows
- 6.8.5 Threading Rules that Affect Windows and ACCEPT Statements
- threads:locking
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- LOCK Statement
- threads:logical operations preserved
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- threads:messaging among
- 6.8.3 Thread Communication
- threads:multiple locks
- LOCK Statement
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- threads:multiprocessor issues
- 6.8.7 Multithreading and Multiprocessor Systems
- threads:pausing
- 6.8.6 Thread Pausing
- threads:priority
- 6.8.4 Thread Priorities
- threads:receiving messages
- RECEIVE Statement
- threads:sending messages
- SEND Statement
- threads:sharing data
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- threads:stopping
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- threads:switch point
- 6.8.4 Thread Priorities
- threads:synchronizing
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- threads:to manage modeless windows
- 6.8 Multiple Execution Threads
- threads:WAIT times out
- WAIT Statement
- TITLE, DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- TITLE, in line drawing
- DISPLAY LINE
- TITLE, with DISPLAY BOX
- DISPLAY BOX
- title:placing in floating window
- DISPLAY FLOATING WINDOW
- tool tips, see pop-up hints
- 3.8.4 Pop-Up Hints
- toolbar: as function keys
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- toolbar:more than one in a window
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- toolbar:placing controls with the UPON phrase
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- toolbar:space occupied by
- DISPLAY TOOL-BAR
- TRACK-THUMB, SCROLL-BAR style
- 5.12 Scroll Bar
- trailing space removal
- STRIP-TRAILING-SPACES
- transaction error codes
- J.4 Transaction Error Codes
- transaction files, compiler option
- 2.1.4 File Options
- transaction log file, how to edit
- 3.6 logutil
- transaction logging
- 5.1.2 The Transaction Logging Process
- 5.1.1.1 Transaction logging
- transaction logging and recovery with AcuServer
- 5.1.10.1 Transaction logging and recovery with AcuServer
- transaction logging, configuration variables used with
- 5.1.7 Configuration Variables
- transaction logging, specifying log files
- 5.1.6 Multiple Log Files
- transaction management
- 5.1 Transaction Management
- transaction management features supported
- 5.1.1.3 Features
- transaction management verbs
- 5.1.3 Transaction Management Verbs
- transaction management, compiler options used with
- 5.1.9 Compiler File Options
- transaction management, file types supported
- 5.1.1.2 File types
- transaction management, overview
- 5.1.1 Overview of Transaction Management
- transaction management, rules for Vision and relative files
- ROLLBACK Statement
- transaction management:filename-LOG configuration variable
- filename-LOG
- transaction, beginning with START
- START Statement
- transactions, effects of UNLOCK
- UNLOCK Statement
- transactions, error codes
- 5.1.8 Transaction Error Handling
- transactions, primary error codes
- J.4.1 Primary Error Codes
- transactions, secondary error codes for error 01
- J.4.2 Secondary Error Codes for Error 01
- TRANSACTION-STATUS codes
- J.4 Transaction Error Codes
- TRANSACTION-STATUS register
- 5.1.8 Transaction Error Handling
- TRANSLATE-TO-ANSI, configuration file entry
- TRANSLATE-TO-ANSI
- Translation of Messages
- 3.5.3 Translation of Messages
- TREE-ROOT-SPACE
- TREE-ROOT-SPACE
- TREE-TAB-SIZE
- TREE-TAB-SIZE
- Tree-View
- 5.16 Tree-View
- troubleshooting installations under UNIX
- A.5.1.3 Troubleshooting
- TrueType fonts, printing
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- truncation of XFD names
- 5.3.3.6 Name Directive
- TRX-HOLDS-LOCKS, configuration file entry
- TRX-HOLDS-LOCKS
U
- UI Terminology
- UI Terminology
- Ultrix, installation
- A.5.1 Extracting the files
- unary minus
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- unary plus
- 6.2 Arithmetic Expressions
- underlined words, in manual
- 1.1.1 Upper-Case and Special-Character Words
- UNFRAMED, CHECK-BOX style
- 5.6 Check-Box
- UNFRAMED, RADIO-BUTTON style
- 5.7 Radio-Button
- UNFRAMED, style
- 3.8.3 Creating the Button
- UNIX network license management
- 2.12.1 UNIX network license management
- UNIX, and COMMIT statement
- COMMIT Statement
- UNIX, and device locking
- 6.1.5 Device Locking Under UNIX
- UNIX, command to check modules for debug mode
- 3.2.3 Getting Object Information
- UNIX, Xenix, Ultrix and Unos machines, installation steps
- A.5 UNIX, Xenix, Ultrix and Unos Machines
- Unloading to Binary and Line Sequential Format
- 3.3.7 Unloading to Binary and Line Sequential Format
- UNLOCK
- 4.2.2 I-O-Control Paragraph
- 6.1.4 Record Locking
- UNLOCK
- UNLOCK statement, general format
- UNLOCK Statement
- UNLOCK THREAD
- 6.8.2 Data Sharing Among Threads
- UNLOCK Statement
- UNLOCK, effect on transactions
- UNLOCK Statement
- Unos, installation
- A.5.1 Extracting the files
- UNSORTED, LIST-BOX
- 5.8 List-Box
- UNSTRING
- UNSTRING
- UNSTRING statement, code examples
- UNSTRING Statement
- UNSTRING statement, general format
- UNSTRING Statement
- UNSTRING statement, highlights for first-time users
- UNSTRING Statement
- UNSTRING, data transfer rules
- UNSTRING Statement
- UNSTRING, overflow condition
- UNSTRING Statement
- updating a menu
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- UPON, omission and -Ca option
- DISPLAY src-item (ANSI format)
- UPON phrase
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- Upper and Lower Case
- 2.1.10 Upper and Lower Case
- Upper-case and Special-Character Words
- Upper-case and Special-Character Words
- upper-case and special-character words in manual
- 1.1.1 Upper-Case and Special-Character Words
- upper-case words, in manual
- Upper-case and Special-Character Words
- uppercase, converting
- C$TOUPPER and C$TOLOWER Routines
- UPPER-LOWER-MAP
- UPPER-LOWER-MAP
- UPPER-LOWER-MAP, configuration file entry
- UPPER-LOWER-MAP
- USAGE clause, syntax rules
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- USAGE HANDLE
- 4.1 Handles
- USAGE HANDLE OF MENU
- 4.1 Handles
- USAGE IS FLOAT
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- USAGE IS INDEX
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- USAGE IS POINTER
- 5.7.1.8 USAGE clause
- USE
- USE
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- USE GROUP directive
- 5.3.3.9 Use Group Directive
- USE statement, general format
- USE Statement
- USE statement, highlights for first-time users
- USE Statement
- USE-MOUSE, configuration file entry
- USE-MOUSE
- user count
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- 3.3.2 Testing File Integrity
- user count, action if non-zero
- 3.3.1 Examining File Information
- user count, resetting
- 3.3.4 Resetting User Counts
- user interface configuration and programming Support
- 1.2.2 Configuration and Programming Support
- user interface features
- 1.1 Overview of User Interface Features
- User Interface Programming
- 1.2.2 User Interface Programming
- User Interface Programming, summary of contents
- 1.2.2 User Interface Programming
- user interface, development strategies
- 1.6.2 Strategies for Supporting Multiple Systems
- user interface, related topics index
- 1.2.3 Index toRelated Topics
- user limit
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- user limit, how to increase
- 2.11 Multiple-User License Management
- user limits on DOS and Windows
- 2.11.1 License Management on DOS and Windows Systems
- user-defined words
- 2.1.1.1 User-defined words
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- User's Guide, summary of contents
- 1.2.1 User's Guide
- USING phrase
- 6.5 Procedure Division Format
- USING phrase, CALL
- CALL Statement
- USING phrase, CHAIN
- CHAIN Statement
- Using shared memory
- 2.12.2 Using shared memory
- utilities, vutil
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
V
- V23-GRAPHICS-CHARACTERS, configuration file entry
- V23-GRAPHICS-CHARACTERS
- V30-MEASUREMENTS, configuration file entry
- V30-MEASUREMENTS
- V31-FLOATING-POINT
- V31-FLOATING-POINT
- validating data
- 6.6 Data Validation
- validating data, not performed when
- 6.6 Data Validation
- VALUE clause in Screen Section
- 5.9.2 VALUE Clause
- VALUE clause, general format
- 5.7.1.14 VALUE clause
- VALUE clause, general rules
- 5.7.1.14 VALUE clause
- VALUE IS MULTIPLE VALUE phrase
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- VALUE OF FILE-ID
- 5.4.8 VALUE OF FILE-ID Clause
- VALUE OF LABEL Clause
- 5.4.7 VALUE OF LABEL Clause
- values, how determined
- EVALUATE Statement
- variable length records
- 5.1.7 File Types
- 6.1 Handling Files
- variables, and debugger
- 3.1.6 Specifying Addresses
- VAR-LENGTH directive
- 5.3.3.10 Var-Length Directive
- VAX COBOL
- 5.7.1.11 SYNCHRONIZED clause
- 2.1.3 Compatibility Options
- 2.3 Compatibility Modes
- VAX COBOL terminal format
- 2.2 Source Format
- VAX COBOL, and COMMIT statement
- COMMIT Statement
- VAX COBOL, and file status codes
- 2.7.3 File Status Codes
- VAX COBOL, compatibility mode
- 2.3 Compiler Compatibility Modes
- VAX COBOL, ERASE
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- DISPLAY src-item
- VAX COBOL, file status codes
- J.1 Introduction
- VAX COBOL, reserved words
- D.1 Introduction
- VAX COBOL, reserved words option
- 2.1.6 Reserved Word Options
- VAX COBOL, terminal source format
- 2.4 Source Formats
- VAX/RMS, undefined File Position Indicator
- READ Statement
- VAX/VMS, filenames
- 2.8.1 File Names Starting with a Hyphen
- VAX/VMS, line sequential files
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- VAX/VMS, sequential files
- 6.1.1 Sequential Files
- V-BUFFER-DATA, configuration file entry
- V-BUFFER-DATA
- V-BUFFERS, configuration file entry
- V-BUFFERS
- V-BUFFERS, performance considerations
- 6.1.8 Performance Considerations
- version command
- 2.1.14 Help, Version Information, and Communication with C Programs
- vertical bars
- Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- 1.1.3 Brackets, Braces and Vertical Bars
- 1.6 Notation
- VERY-HEAVY, FRAME style
- 5.10 Frame
- video attributes
- 4.6.3 Video Attributes
- video attributes, terminals with non-hidden
- 4.5 Restricted Attribute Handling
- video intensity, compiler options
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- Video Options
- 2.1.8 Video Options
- video, control with SCREEN variable
- 4.4.2 The SCREEN Option
- view
- 3.1.3 Debugger Commands
- V-INTERNAL-LOCKS, configuration file entry
- V-INTERNAL-LOCKS
- vio
- 3.4 File Transfer Utility-vio
- vio, examples
- 3.4.3 vio Examples
- vio, file transfer utility
- 3.4 File Transfer Utility-vio
- vio, known limitations
- 3.4.4 Known Limitations
- vio, MS-DOS considerations
- 3.4.2 MS-DOS Considerations
- vio, options
- 3.4.1 vio Options
- virtual screen, defined
- 1.4 Windowing Concepts
- Vision
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
- Vision file system, described
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- Vision file, mapping to a different directory
- NAME_EXT
- Vision secondary error codes for error 98s
- J.3 Vision Secondary Error Codes for Error 98s
- Vision Version 3
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- Vision version 4
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- Vision Version 4, file naming conventions
- 6.1.3 Indexed Files
- Vision, secondary error codes for error 98s
- J.3 Vision Secondary Error Codes for Error 98s
- V-LOCK-METHOD, configuration file entry
- V-LOCK-METHOD
- VMS
- 2.7.5 File Handling Options
- VMS and Open VMS installation
- A.6 VMS and Open VMS Machines
- VMS file utilities
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
- VMS, and COMMIT statement
- COMMIT Statement
- V-READ-AHEAD, configuration file entry
- V-READ-AHEAD
- V-SEG-SIZE, configuration file entry
- V-SEG-SIZE
- vutil, check for file integrity
- 3.3.2 Testing File Integrity
- vutil, converting a C-ISAM file
- 3.3.11 Converting C-ISAM Files
- vutil, converting a Micro Focus file
- 3.3.12 Converting Micro Focus Files
- vutil, converting an RM/COBOL-85 indexed file
- 3.3.10 Converting RM/COBOL-85 Indexed Files
- vutil, creating empty files
- 3.3.6 Creating Empty Files
- vutil, creating empty files-indexed format
- 3.3.6 Creating Empty Files
- vutil, creating empty files-interactive version
- 3.3.6 Creating Empty Files
- vutil, creating empty files-non interactive version
- 3.3.6 Creating Empty Files
- vutil, creating empty files-sequential and relative
- 3.3.6 Creating Empty Files
- vutil, examining file information
- 3.3.1 Examining File Information
- vutil, extracting records
- 3.3.5 Extracting Records from a File
- vutil, loading a file
- 3.3.8 Loading a File
- vutil, rebuilding files
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- vutil, rebuilding files--locking options
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- vutil, rebuilding files--naming temporary files
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- vutil, rebuilding files-new blocking factor
- 3.3.3 Rebuilding Files
- vutil, resetting user counts
- 3.3.4 Resetting User Counts
- vutil, tree option
- 3.3.13 Miscellaneous Commands
- vutil, uploading to binary sequential format
- 3.3.7 Unloading to Binary and Line Sequential Format
- vutil, uploading to line sequential format
- 3.3.7 Unloading to Binary and Line Sequential Format
- vutil, utilities
- 3.3 File Utilities-vutil
- vutil, version option
- 3.3.13 Miscellaneous Commands
- V-VERSION, configuration file entry
- V-VERSION
- Vx compile-time option
- 4.3.1 Key Mapping
W
- W$BITMAP Routine
- W$BITMAP Routine
- W$BITMAP, library routine to manipulate bitmaps
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- W$BROWSERINFO
- W$BROWSERINFO
- W$FONT
- W$FONT Routine
- 4.6 Fonts
- W$FORGET Routine
- W$FORGET Routine
- W$GETC Routine
- W$GETC Routine
- W$GETURL Routine
- W$GETURL Routine
- W$GETVARIANT Routine
- W$GETVARIANT Routine
- W$KEYBUF Routine
- W$KEYBUF Routine
- W$MENU
- 8.8 Common Menu Operations
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- W$MENU, to attach a menu to a floating window
- 2.6 Menus and Floating Windows
- W$MOUSE
- W$MOUSE Routine
- 7.6 W$MOUSE Library Routine
- W$PALETTE Routine
- W$PALETTE Routine
- W$SETVARIANT Routine
- W$SETVARIANT Routine
- W$STATUS Routine
- W$STATUS Routine
- W$TEXTSIZE Routine
- W$TEXTSIZE Routine
- WAIT
- WAIT
- 6.8.1 Thread Fundamentals
- WAIT Statement
- WAIT Statement
- WAIT, general format
- WAIT Statement
- WAIT-FOR-ALL-PIPES, configuration file entry
- WAIT-FOR-ALL-PIPES
- WAIT-FOR-FILE-ACCESS
- WAIT-FOR-FILE-ACCESS
- WAIT-FOR-LOCKS, configuration file entry
- WAIT-FOR-LOCKS
- WARNINGS, configuration file entry
- WARNINGS
- WARNING_ON_RECURSIVE_ACCEPTS, configuration file entry
- WARNING_ON_RECURSIVE_ACCEPTS
- WAV file support
- WIN$PLAYSOUND Routine
- WBITMAP-DESTROY
- W$BITMAP Routine
- WBITMAP-DESTROY, to remove bitmap
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- WBITMAP-DISPLAY
- W$BITMAP Routine
- WBITMAP-LOAD, to load a bitmap
- 3.8.2 Loading Bitmaps
- W-CHECKED
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- W-CONVERSION-ERROR
- ACCEPT Statement
- W-DISABLED
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- Web, deploying on the
- W$GETURL Routine
- W-EVENT
- ACCEPT Statement
- WFONT-CHOOSE-FONT
- W$FONT Routine
- WFONT-DATA
- W$FONT Routine
- WFONT-DESCRIBE-FONT
- W$FONT Routine
- WFONT-GET-CLOSEST-FONT
- W$FONT Routine
- WFONT-GET-FONT
- W$FONT Routine
- WFONT-SUPPORTED
- W$FONT Routine
- WHEN directive
- 5.3.3.11 When Directive
- WHEN SET TO FALSE
- 5.7.1.14 VALUE clause
- WHITE-FILL
- WHITE-FILL
- 9.9.1 Background Brush Color
- wide font
- 5.4 Entry-Field
- WIDTH, BAR special property
- 5.11 Bar
- WIDTH-IN-CELLS, control style
- 5.2 Global Styles
- WIN$PLAYSOUND library routine
- WIN$PLAYSOUND Routine
- WIN$PRINTER library routine
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WIN$PRINTER:error codes
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WIN$VERSION library routine
- WIN$VERSION Routine
- WIN$VERSION Routine
- WIN$VERSION Routine
- WIN3-CLIP-CONTROLS, configuration file entry
- WIN3-CLIP-CONTROLS
- WIN3-EF-PADDED, configuration file entry
- WIN3-EF-PADDED
- WIN3-GRID, configuration file entry
- WIN3-GRID
- WIN32-3D
- WIN32-3D
- window events
- 6.1 Window Events
- Window Size
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- window title font
- WINDOW-TITLE
- window types
- 1.5 ACUCOBOL-GT Window Types
- window, color inherited
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- window, restoration
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- window, save-area data of
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- window, scroll and wrap state of pop-up
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- window,shadows
- DISPLAY WINDOW
- window,title modification
- DISPLAY UPON WINDOW TITLE
- window:current
- 2.3 Active and Current Windows
- window:modal
- 2.1 Overview
- window:modeless
- 2.1 Overview
- windowing concepts
- 1.4 Windowing Concepts
- Windows 95, installation
- A.4 Windows Machines
- Windows Help
- 10.4 Windows Help
- Windows NT, installation
- A.4 Windows Machines
- Windows NT:specifics
- M.3 32-bit Windows
- Windows SDK
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- Windows Software Development Kit
- 1.2.4 GUI Development with Third Party Kits and Tools
- Windows spooler
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- Windows, and programming in C
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- Windows, compiling under
- A.4.3 Compiling under Windows
- Windows, executing the runtime for
- .c4.A.4.4 Running your programs
- Windows, hardware and software requirements
- A.4.1 Hardware and software requirements
- Windows, installation
- A.4.2 Installation steps for Windows
- Windows, installation under
- A.4 Windows Machines
- Windows, Microsoft:automatic adjustments for
- 1.3 Microsoft Windows Operating Systems
- Windows, multiple instances of a program
- M.2.6 Using the SDK
- Windows, printer and spooler issues
- A.4.5 Printing and spooler issues with Windows
- Windows, questions asked
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- Windows, running the debugger under
- 3.1.1 Entering the Debugger
- Windows:calling DLLs
- M.2.4 Calling DLLs
- windows:changing with the MODIFY statement
- MODIFY Statement
- Windows:Common Dialog Boxes
- 11.1.1 Regarding Windows
- Windows:extra keys available
- M.2.2 Keyboard Differences
- Windows:Graphics Device Interface (GDI)
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- Windows:print spooler
- Routine to Handle the Windows Print Spooler
- Windows:print support
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- windows:resizing
- RESIZE-FREELY
- windows:retrieving information about
- INQUIRE Statement
- Windows:retrieving operating system information
- WIN$VERSION Routine
- Windows:specific details
- M.2 16-bit Windows
- WINDOW-TITLE, configuration file entry
- WINDOW-TITLE
- WIN-ERROR-HANDLING
- M.2.3 Hardware Error Handling
- WIN-ERROR-HANDLING
- M.3.3 Hardware Error Handling
- WINHELP ($WINHELP) library routine
- $WINHELP Routine
- WINHELP ($WINHELP) library routine:part of Windows Help facility
- 10.4 Windows Help
- winprint.def
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-DATA
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-DEVICE-INCAPABLE
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-GET-CAPABILITIES
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-GET-PAGE-LAYOUT
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-GET-SETTINGS
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-GET-SETTINGS-SIZE
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-PRINT-BITMAP
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-SET-FONT
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-SET-SETTINGS
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-SET-STD-FONT
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-SETUP
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-SPOOLER-CLOSED
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINPRINT-SUPPORTED
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WINSOCK.DLL
- 5.2.1 System Requirements
- winvers.def
- WIN$VERSION Routine
- WINVERSION-DATA group item
- WIN$VERSION Routine
- WITH DEBUGGING MODE
- 4.1.1 Source-Computer Paragraph
- WMENU-ADD
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- WMENU-BLOCK
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-CHANGE
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- WMENU-CHECK
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- WMENU-DELETE
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-DESTROY
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-DESTROY-DELAYED
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-DISABLE
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-ENABLE
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-GET-BLOCK
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-GET-MENU
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-NEW
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-REFRESH
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-SET-BLOCK
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-SHOW
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-UNBLOCK
- W$MENU Routine
- WMENU-UNCHECK
- W$MENU Routine
- W-MESSAGE
- ACCEPT Statement
- W-NO-FIELDS
- ACCEPT Statement
- Working-Storage, general format
- 5.5 WORKING-STORAGE Section
- WPALETTE-CHOOSE-COLOR
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPALETTE-GET-COLOR
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPALETTE-NUM-COLORS
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPALETTE-SET-COLOR
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPALETTE-SET-USER-COLOR
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPALETTE-SUPPORTED
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPALETTE-UPDATE
- W$PALETTE Routine
- WPRTDATA-COLUMNS-PER-PAGE
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WPRTDATA-LINES-PER-PAGE
- WIN$PRINTER Routine
- WRAP
- 4.4.3 Additional Configuration Variables
- WRAP
- WRITE
- WRITE
- WRITE statement, and LINAGE clause
- 5.4.11 LINAGE Clause
- WRITE statement, general format
- WRITE Statement
- WRITE, and LINAGE clause
- WRITE Statement
- WRITE, general rules
- WRITE Statement
- WRITE, invalid key condition
- WRITE Statement
- WRITE, with ADVANCING
- WRITE Statement
- WRITE, without carriage-control
- WRITE Statement
- WS_CLIPCHILDREN
- WIN3-CLIP-CONTROLS
- W-SEPARATOR
- W$MENU Routine
- 8.10 W$MENU Library Routine
- WSOCK32.DLL
- 5.2.1 System Requirements
- W-TIMEOUT
- ACCEPT Statement
- Wyse 50
- 4.5 Restricted Attribute Handling
X
- XENIX, and setcolor
- 4.4.1 Adding Color
- Xenix, installation
- A.5.1 Extracting the files
- XFD Files
- 5.3 XFD Files
- XFD name
- 5.3.1 Defaults Used in XFD Files
- XFD-DIRECTORY, configuration file entry
- XFD-DIRECTORY
- XFDs
- 5.3.2 Using Directives
- 5.3 XFD Files
Z
- ZERO condition
- 6.3.3 Sign Condition
- -Zx
- 5.3 XFD Files