5.3.5 DELETE Command
Use the SQL statement DELETE to delete one or more rows from a table.
Syntax
DELETE FROM <table-name>
[WHERE <condition>]
This command deletes rows whose values satisfy the WHERE condition. The
format of the WHERE clause is the same as it is in the SELECT command. If there is no WHERE clause, all rows are deleted.
If the WHERE condition is included, but no rows satisfy the condition, the
command does nothing, and it does not report an error.
Example
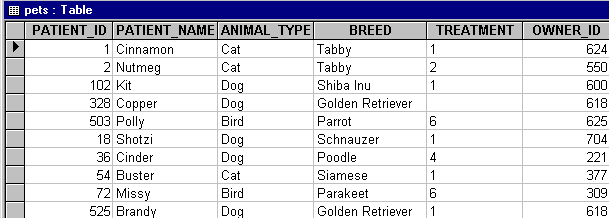
DELETE FROM pets
WHERE ANIMAL_TYPE = 'Rodent'
This statement deletes all the rows that have the column "animal_type"
containing the value "Rodent." The revised table looks similar to this:
Important: Be sure to include a WHERE clause in your statement. If you do not, all the
rows of the table will be deleted. For example,
DELETE FROM PETS
deletes all the rows in the table called "pets."
If a data source is designated as read-only and the data is linked, users
cannot delete rows from the table, and therefore, records from in the data file.
Read Only is the default setting. To enable users to delete rows from the
table, and the data file, clear the Read Only checkbox on the Advanced tab of the
AcuODBC Configuration property sheet (or the AcuODBC Server Configuration
property sheet if this is a remote DSN).