

Sybase: Installation steps on the UNIX
client
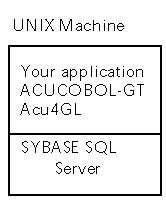
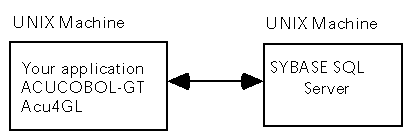
Acu4GL will communicate with Sybase version
10.0 or later. The client (your application) and the server (the RDBMS)
may be located on the same UNIX machine, or on different UNIX machines.
The server may also be located on a Windows NT machine:

To install the Acu4GL interface, first perform the following steps on the UNIX client machine:
Step One: Install Sybase client library
The Open Client DB-Library/C from Sybase (version 10.0 or later) must be installed on the client machine before you install Acu4GL for Sybase. Follow the installation instructions in your Sybase documentation.
Step Two: Create a makefile
The script syb_inst is an interactive shell script that determines which libraries your version of Sybase has, and then creates a makefile suitable for linking Acu4GL with an ACUCOBOL-GT runtime for UNIX. It also generates the SQL script used to install ACUCOBOL-GT stored procedures. In the instructions below, bold italicized text within a message indicates that the script will insert what you had previously typed.
Execute the shell script syb_inst by typing the following on your client machine:
sh syb_inst <enter>
NOTE
You may exit the script at any time by pressing the system interrupt key (usually control-C).
If you entered just syb_inst <enter> instead of the full command, this message may appear:
VAL=0: command not found
VAL: Undefined variable
This can be fixed by entering sh syb_inst.
When the script begins executing, you will see the following message:
During the execution of this script, we will create an SQL script which you will need to execute from isql, using a command like:
"isql -Usa -Ppassword < syb_inst.sql"
This script will add some stored procedures, and create some tables in a database that you specify during the execution of this script.
In order to implement locking from ACUCOBOL-GT, we need to create a lock table. This should be a pretty small table, but we need to decide which database to create this table in. You should now enter the name of the database you want the lock tables created in. If the database does not exist, it will be created.
The following question will then be asked repeatedly until you enter a valid database name:
Which database would you like to create this table in?
This database will eventually be located on your server machine. Enter a valid database name. (Invalid names are master, model, temp or sybsystemprocs.) Names must start with a letter or underscore, must contain only letters, digits and underscores, and may be up to 30 characters long. Any other entry will be modified.
Next you will see the following message:
Saving any old version of syb_inst.sql...
Old versions of syb_inst.sql are saved to syb_instnnn,sql where nnn starts at 001 and goes to 999. If a file syb_inst.sql exists, you will see:
Saving syb_inst.sql as syb_instnnn.sql
for some value of nnn. Then you will see:
Creating syb_inst.sql...
This uses the file syb_inst.in as a template, and creates syb_inst.sql, using the database name you entered above.
You will also see:
Creating cblconfig.syb...
This is a sample file of configuration variables you may want to add to your cblconfig file.
You will then see the following message:
In order to use the Acu4GL for Sybase interface, you need to relink the runtime system. We are assuming that the Makefile that came with your runtime system still has the "FSI_SUBS=" and FSI_LIBS=" lines in it, and will base our changes on that Makefile. However, we will create a new file called Makefile.syb, that has these changes in it.
Do you want to set up the Makefile for this system?
Type y or Y to continue.
You will then see the following message:
We next need to determine where you
have installed the
SYBASE client libraries.
The following prompt will repeat until you enter the directory that contains the Sybase files:
Enter the directory where the SYBASE client libraries are installed
Type the full pathname of the directory containing the Sybase client libraries, followed by <enter>. Note that this is the directory that contains the Sybase lib directory. For example, if the full path for the file libsybdb.a is /usr/sybase/lib/libsybdb.a, then you would type /usr/sybase.
The script checks for a file lib/libsybdb.a in the directory you entered. You will then see one of the following messages:
We seem to have the ACUCOBOL-GT library files in this directory.
We need to find the ACUCOBOL-GT library
files...
Enter the directory where ACUCOBOL-GT
is installed:
If you are asked to enter the directory name, type the full pathname of the directory containing ACUCOBOL-GT, followed by <enter>.
Before the Makefile is created, we need to check for some alternate optional libraries. You will see the message:
Checking for -lnsl or -lnsl_s
If one of the libraries exists, you will see:
using -lnsl
-or-
using -lnsl_s
If you instead see a message like this one:
syb_inst: cc: not found
then it's likely that your PATH environment variable does not include the location of your compiler. In this case, exit from the script, fix the PATH variable, and start the script again.
Finally, you will see the message:
Creating Makefile.syb ...
Makefile.syb created. You should
be able to execute "make
-f
Makefile.syb"
and the script will exit.
Step Three: Move the makefile
Copy Makefile.syb to the ACUCOBOL-GT library subdirectory if it is not already there.
Now you are ready to relink your ACUCOBOL-GT runtime.
Step Four: Link the runtime system
Make sure you are in the ACUCOBOL-GT library directory. This contains the Makefile.syb file.
At the UNIX prompt, type:
make -f Makefile.syb <enter>
This will compile sub.c and filetbl.c, and will then link the runtime system.
Step Five: Verify the link
Type:
./runcbl -vv <enter>
to verify the link. This will return version information on all of the products linked into your runtime system. Make sure it reports the version of Acu4GL for Sybase.
Shared libraries
If you have relinked the ACUCOBOL-GT runtime and receive an error message of this type when you try to execute it:
Could not load library; no such file or directory
Can't open shared library . . .
this may mean that your operating system is using shared libraries and cannot find them. This can occur even if the shared libraries reside in the same directory where you are currently located.
Different versions of the UNIX operating system resolve this in different ways, so it is important that you consult your UNIX documentation to resolve this error.
Some versions of UNIX require that you set an environment variable that points to shared libraries on your system.
For example, on an IBM RS/6000 running AIX 4.1, the environment variable LIBPATH must point to the directory where the shared libraries are located.
On HP/UX, the environment variable that must be set to point to shared libraries is SHLIB_PATH. On UNIX SVR4, the environment variable is LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
Be sure to read the system documentation for your operating system to determine the appropriate way to locate shared libraries.
A second way to resolve this type of error is to link the libraries into the runtime with a static link. Different versions of the C development system use different flags to accomplish this link. Please consult the documentation for your C compiler to determine the correct flag for your environment.
Step Six: Copy runcbl to the correct directory
Copy the newly created file runcblto a directory mentioned in your execution path. This file needs to have execute permission for everyone who will be using the compiler or runtime system.
The ACUCOBOL-GT license file for the runtime (runcbl.alc) and the license file for the Acu4GL interface to Sybase (runcbl.ylc) must be copied into the same directory as the runtime executable. If you rename your runtime executable, be sure to rename your license files to use the same base name, with the extensions unchanged. For example, if you rename your runtime to be myprog, then the license file for the Acu4GL interface for Sybase should be renamed myprog.ylc, and the license file for the runtime should be renamed myprog.alc.
The remaining files can be left in the directory to which they were unloaded from the distribution medium.
Step Seven: Use rehash
If you are using the C-shell, enter the command rehash. This tells the C-shell that there is a new executable in the path.
This completes the installation process on the client machine.